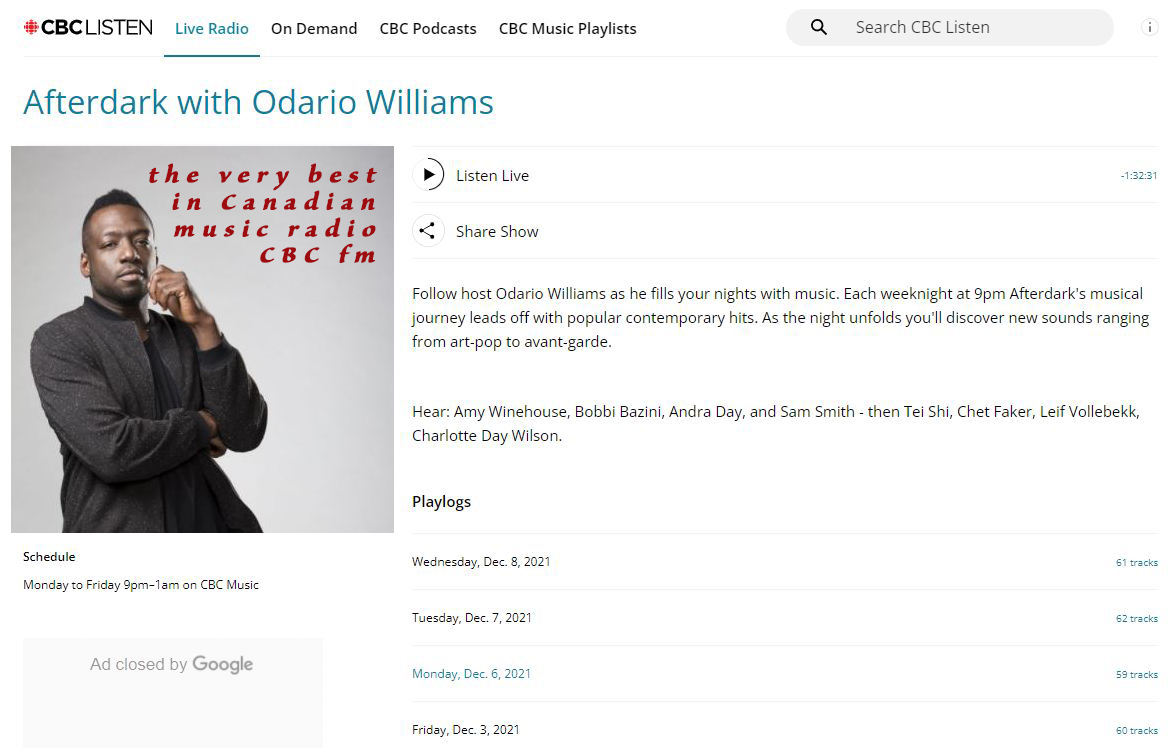
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Circles
Posts
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Very best late night music radio station, we recommend, AFTERDARK With Odario Williams on CBC radio FM Canada. Fine selection of international sounds sprinkled throughout: https://cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark #AFTERDARK #CBCfm #radio #music #Canada #world #Europe #Asia #Africa #SouthAmerica
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Videos
In today’s episode of “Direct Impact,” Rick Sanchez explores the underlying motivations behind America’s involvement in Ukraine, citing statements from Hungarian leader Victor Orban and US Senator Lindsey Graham that suggest financial interests are at play. Rick also highlights Tucker Carlson’s interview with Congressman Thomas Massie, who discusses the powerful influence of the Israel Lobby, AIPAC, over US politicians. Finally, Rick has a discussion with Kevork Almassian, host of Syriana Analysis, to uncover the reasons behind Syria’s ongoing crisis.
On this episode of The MO, host Manila Chan delves into an ntriguing discussion with Timothy J. Gordon about Pope Francis. They explore the Pope's leadership style and the Church's stance on land ownership, offering insights into the complexities of these issues within the Catholic community.
Welcome to The Daily Wrap Up, a concise show dedicated to bringing you the most relevant independent news, as we see it, from the last 24 hours.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/alshifa-massacre-israel-iran-syria
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get TLAV Apparel:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
https://tlavfreespeech.itemorder.com/shop/home/
SAVE TLAV Campaign:
https://www.givesendgo.com/SaveTLAV
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.paychute.com/c/b7c68a5b-d437-444c-973b-e0413a5e07c3
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
Support TLAV through Autonomy:
Join Autonomy:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/29887/QZmKjVCA
Ryan Cristián’s Objectivity Course:
https://marketplace.autonomyagora.com/objective-research
Richard Grove’s Course:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/2147526145/QZmKjVCA
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TLAVagabond
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/tlavagabond.bsky.social
#TLAVPirateStreams #TheDailyWrapUp #TheLastAmericanVagabond
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Circles
Videos
In today’s episode of “Direct Impact,” Rick Sanchez explores the underlying motivations behind America’s involvement in Ukraine, citing statements from Hungarian leader Victor Orban and US Senator Lindsey Graham that suggest financial interests are at play. Rick also highlights Tucker Carlson’s interview with Congressman Thomas Massie, who discusses the powerful influence of the Israel Lobby, AIPAC, over US politicians. Finally, Rick has a discussion with Kevork Almassian, host of Syriana Analysis, to uncover the reasons behind Syria’s ongoing crisis.
On this episode of The MO, host Manila Chan delves into an ntriguing discussion with Timothy J. Gordon about Pope Francis. They explore the Pope's leadership style and the Church's stance on land ownership, offering insights into the complexities of these issues within the Catholic community.
Welcome to The Daily Wrap Up, a concise show dedicated to bringing you the most relevant independent news, as we see it, from the last 24 hours.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/alshifa-massacre-israel-iran-syria
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get TLAV Apparel:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
https://tlavfreespeech.itemorder.com/shop/home/
SAVE TLAV Campaign:
https://www.givesendgo.com/SaveTLAV
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.paychute.com/c/b7c68a5b-d437-444c-973b-e0413a5e07c3
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
Support TLAV through Autonomy:
Join Autonomy:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/29887/QZmKjVCA
Ryan Cristián’s Objectivity Course:
https://marketplace.autonomyagora.com/objective-research
Richard Grove’s Course:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/2147526145/QZmKjVCA
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TLAVagabond
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/tlavagabond.bsky.social
#TLAVPirateStreams #TheDailyWrapUp #TheLastAmericanVagabond
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Welcome to The Daily Wrap Up, a concise show dedicated to bringing you the most relevant independent news, as we see it, from the last 24 hours.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/bio-nanothings-israel-yemen-iraq
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get TLAV Apparel:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
https://tlavfreespeech.itemorder.com/shop/home/
Support TLAV through Autonomy:
Join Autonomy:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/29887/QZmKjVCA
Ryan Cristián’s Objectivity Course:
https://marketplace.autonomyagora.com/objective-research
Richard Grove’s Course:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/2147526145/QZmKjVCA
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TLAVagabond
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
BlueSky: https://bsky.app/profile/tlavagabond.bsky.social
#TLAVPirateStreams #TheDailyWrapUp #TheLastAmericanVagabond
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Joining me today is Kevork Almassian, here to discuss a very concerning development that his research has uncovered and his sources in Syria have confirmed; the US government appears to be considering the assassination of the Syrian president, Bashar al-Assad. We go over why this is being considered, what the geopolitical implication would be, and how this directly affects the ongoing siege against Gaza.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/kevork-almassian-interview-11-4-23
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get TLAV Apparel:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
https://tlavfreespeech.itemorder.com/shop/home/
Support TLAV through Autonomy:
Join Autonomy:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/29887/QZmKjVCA
Ryan Cristián’s Objectivity Course:
https://marketplace.autonomyagora.com/objective-research
Richard Grove’s Course:
https://www.universityofreason.com/a/2147526145/QZmKjVCA
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TLAVagabond
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
#TheLastAmericanVagabond #MedicalKidnapping #KevorkAlmassian
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Posts
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Very best late night music radio station, we recommend, AFTERDARK With Odario Williams on CBC radio FM Canada. Fine selection of international sounds sprinkled throughout: https://cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark #AFTERDARK #CBCfm #radio #music #Canada #world #Europe #Asia #Africa #SouthAmerica
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
For the very best in Japanese news, social news and entertainment MIDNIGHT AT THE COFFEE SHOP recommends: TJS Radio. Just click here: https://radio.net/s/tjsradio #Japan #TJSradio #radio #Japan #NorthAmerica #Japanese #Canada #news #entertainmentNews #social
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
The Etihad Airways Damascus Office provides professional help for flights and questions, ensuring smooth travel arrangements. Visit our easily accessible office to get individualised care and effective solutions. With our committed staff in Damascus, enjoy the luxury and dependability of Etihad Airways. Make confident and simple travel plans
visit us : https://airlinesofficeinfo.com/offices/etihad-airways-damascus-office-in-syria/