Đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024 đã được công bố với những cầu thủ tài năng và kinh nghiệm trên đấu trường bóng đá quốc tế. Tại Euro năm nay, đội tuyển Ba Lan được kỳ vọng sẽ mang đến những trận đấu hấp dẫn cho người hâm mộ. Cùng tìm hiểu những thông tin chi tiết được chia sẻ trong bài viết dưới đây tại Euro88.me về đội bóng quốc gia của Ba Lan.
Giới thiệu về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Đội tuyển bóng đá quốc gia Ba Lan là đội tuyển chính thức của đất nước này, do Hiệp hội bóng đá Ba Lan quản lý. Họ đã thi đấu trận đấu quốc tế đầu tiên vào năm 1921 tại Budapest gặp Hungary.
Lịch sử bóng đá của Ba Lan phản ánh sự phức tạp của lịch sử đất nước này, với sự chi phối của ba đế chế: Nga, Áo và Đức vào cuối thế kỷ 19. Tuy nhiên, tình yêu bóng đá không bao giờ phai nhạt của người Ba Lan đã tạo ra một đội tuyển độc lập. Sau những biến động lịch sử, Ba Lan đã tái thiết đội tuyển quốc gia của mình.
Ba Lan đã tham dự World Cup đầu tiên vào năm 1938 và sau đó phải chờ đến năm 1974 mới trở lại. Họ đã đạt được thành công với vị trí thứ ba tại hai kỳ World Cup vào các năm 1974 và 1982. Ba Lan chỉ tham dự Euro lần đầu vào năm 2008 và thành tích tốt nhất của họ là lọt vào tứ kết tại Euro năm 2016.
Thành tích của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Trước khi tìm hiểu về đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 và đánh giá tiềm năng tiến xa của đội tuyển, bạn cần hiểu rõ về thành tích của họ trong vòng loại và những mùa giải trước để có nhận định chính xác nhất.
Hành trình tại vòng loại của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Ba Lan đã thất bại ở bảng E vòng loại Euro 2024, gặp các đối thủ như Albania, CH Séc, Moldova và Quần đảo Faroe. Họ chỉ có được 11 điểm sau 8 trận đấu, bao gồm 3 trận thắng, 2 trận hòa và 3 trận thua. “Đại bàng” Ba Lan xếp thứ ba sau Albania và Cộng hoà Séc.
Điều này cũng có nghĩa là đội phải giành vé qua vòng play-off để tiếp tục tham dự VCK Euro 2024. Trên hành trình gian khổ này, đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 đã giành chiến thắng ấn tượng 5-1 trước Estonia trong trận bán kết và chiến thắng căng thẳng 5-4 trong loạt đá luân lưu với xứ Wales ở trận chung kết.
Thành tích đội tuyển Ba Lan qua các kỳ Euro
Ba Lan đã tham dự 5 vòng chung kết Giải vô địch bóng đá châu Âu, trong đó năm 2012 là đồng chủ nhà (cùng với Ukraina). Thành tích nổi bật nhất là khi họ vào được tứ kết Euro 2016.
Dưới đây là bảng tổng kết thành tích của Ba Lan tại các kỳ Euro:
1960 đến 2004: Không vượt qua vòng loại
Áo – Thụy Sĩ 2008: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Ba Lan – Ukraina 2012: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Pháp 2016: Dừng chân tại Tứ kết
Liên minh châu Âu 2020: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Đức 2024: Vượt qua vòng loại
Nhìn chung, Ba Lan đã tham dự 5 trong tổng số 17 kỳ Euro, và chỉ một lần vào được tứ kết. Tại Euro 2024, đội tuyển Ba Lan được kỳ vọng sẽ tạo ra thành tích mới cho bóng đá nước nhà.
Kết quả bóng đá EURO
Danh sách các cầu thủ trong đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Dưới đây là danh sách các cầu thủ được chọn vào đội hình của Đội tuyển Bóng đá Quốc gia Ba Lan tham dự Euro 2024. Danh sách đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 bao gồm những cầu thủ có khả năng chiến đấu mạnh mẽ và là niềm hy vọng cho người hâm mộ trong hành trình chinh phục giải đấu lớn này.
Đánh giá về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Bước vào Vòng chung kết Euro 2024, đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 nhận được nhiều kỳ vọng từ người hâm mộ. Bên cạnh đó, họ cũng gặp phải nhiều thách thức và bất lợi tại vòng bảng của mình. Cùng đánh giá về đội với những thông tin sau:
Huấn luyện viên Michal Probierz
Michal Probierz, sinh ngày 24 tháng 9 năm 1972, là một huấn luyện viên bóng đá người Ba Lan và cựu cầu thủ. Ông hiện đang là người phụ trách đội tuyển quốc gia Ba Lan tại giải đấu Euro 2024. Trong sự nghiệp cầu thủ, ông chơi ở vị trí tiền vệ và chủ yếu thi đấu cho Gornik Zabrze.
Với vai trò là huấn luyện viên, ông đã hai lần đoạt Cúp Ba Lan và Siêu cúp Ba Lan, một lần với Jagiellonia Bialystok vào năm 2010 và một lần với Cracovia vào năm 2020. Ông đã dẫn dắt đội U21 Ba Lan vào năm 2022 trước khi chuyển sang dẫn dắt đội tuyển quốc gia Ba Lan vào năm 2023. Sau đó, ông đã dẫn dắt đội tuyển quốc gia giành quyền tham dự UEFA Euro 2024.
Cầu thủ trụ cột của đội Robert Lewandowski
Trong đội hình Ba Lan Euro đã có sự góp mặt của Robert Lewandowski – một trong những tiền đạo hàng đầu tại châu Âu. Hiện tại, cầu thủ này đang thi đấu cho câu lạc bộ Barcelona.
Lewandowski, sinh năm 1988, được coi là một trong những tiền đạo hàng đầu trên thế giới. Anh đang trải qua những năm cuối sự nghiệp và được hy vọng sẽ giúp Ba Lan tiến xa ở giải đấu này.
Bảng đấu của đội tuyển tại VCK Euro 2024
Bảng đấu của đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 đã được bốc thăm là Bảng D, bao gồm 4 đội tuyển: Pháp, Hà Lan, Áo và Ba Lan. Pháp được đánh giá là một trong những ứng cử viên hàng đầu cho chức vô địch châu Âu năm nay.
Hà Lan xếp vị trí sau nhưng đội tuyển này có một hàng thủ ấn tượng với nhiều cầu thủ chất lượng. Tuy nhiên, người hâm mộ lo lắng liệu Depay, Gakpo và Weghorst có đủ khả năng ghi bàn để gánh vác nhiệm vụ cho đội bóng hay không.
Nhìn chung, hai đội bóng trên có sự chênh lệch lớn so với các đội còn lại trong bảng D. Tuy nhiên, Áo được đánh giá có phần nhỉnh hơn so với Ba Lan về khả năng đi tiếp nhờ vào màn trình diễn ấn tượng gần đây tại Euro 2024.
Với lịch sử bóng đá lâu đời và sự góp mặt của những cầu thủ kinh nghiệm, Ba Lan với Lewandowski là mối đe dọa đối với hàng thủ của các đội khác. Nhưng thực tế, họ đã có phong độ kém trong vòng loại và cần phải dựa vào may mắn để giành tấm vé đi tiếp ở Vòng chung kết Euro 2024.
Lịch thi đấu của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Lời kết
Với những thông tin được chia sẻ tại euro88.me, hy vọng bạn đã có những thông tin chi tiết về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024. Tuy chưa có nhiều thành tích ấn tượng tại Euro nhưng đội tuyển Ba Lan vẫn được kỳ vọng sẽ mang đến những trận đấu hấp dẫn cho người hâm mộ bóng đá thế giới.
Tham khảo chi tiết tại: https://euro88.me/doi-hinh-ba-lan-euro-2024/
People
Circles
Posts
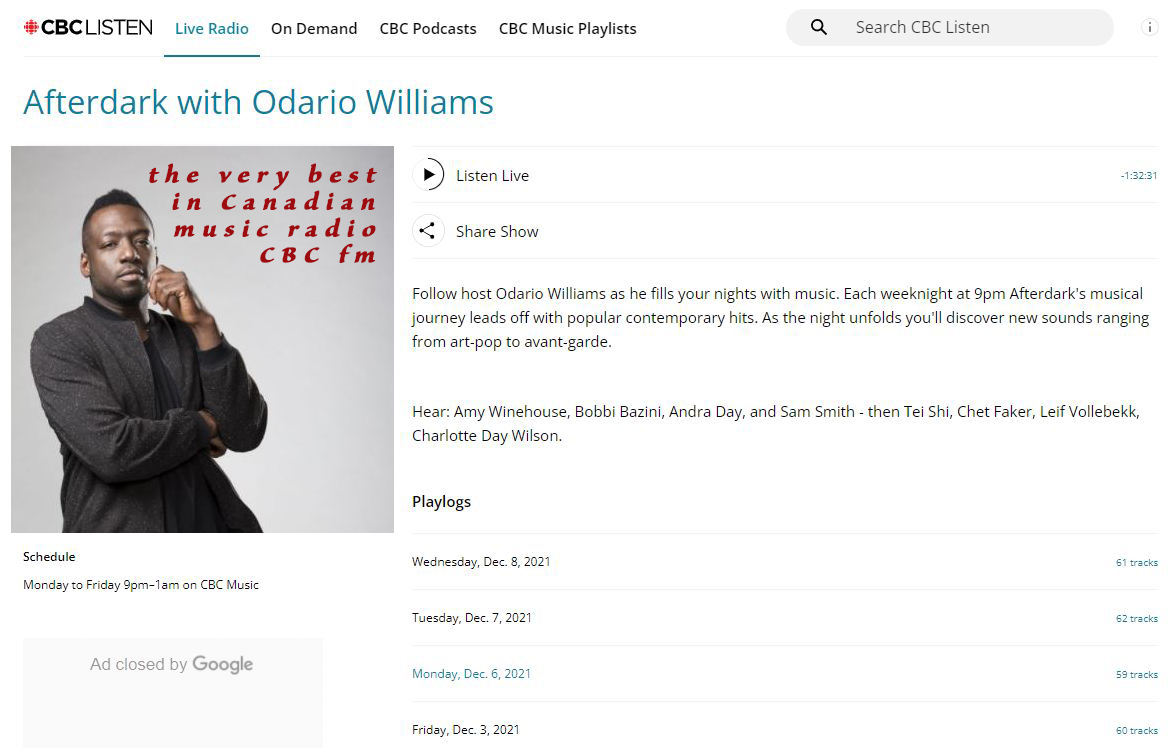
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Videos
People
Circles
Videos
Posts
Đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024 đã được công bố với những cầu thủ tài năng và kinh nghiệm trên đấu trường bóng đá quốc tế. Tại Euro năm nay, đội tuyển Ba Lan được kỳ vọng sẽ mang đến những trận đấu hấp dẫn cho người hâm mộ. Cùng tìm hiểu những thông tin chi tiết được chia sẻ trong bài viết dưới đây tại Euro88.me về đội bóng quốc gia của Ba Lan.
Giới thiệu về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Đội tuyển bóng đá quốc gia Ba Lan là đội tuyển chính thức của đất nước này, do Hiệp hội bóng đá Ba Lan quản lý. Họ đã thi đấu trận đấu quốc tế đầu tiên vào năm 1921 tại Budapest gặp Hungary.
Lịch sử bóng đá của Ba Lan phản ánh sự phức tạp của lịch sử đất nước này, với sự chi phối của ba đế chế: Nga, Áo và Đức vào cuối thế kỷ 19. Tuy nhiên, tình yêu bóng đá không bao giờ phai nhạt của người Ba Lan đã tạo ra một đội tuyển độc lập. Sau những biến động lịch sử, Ba Lan đã tái thiết đội tuyển quốc gia của mình.
Ba Lan đã tham dự World Cup đầu tiên vào năm 1938 và sau đó phải chờ đến năm 1974 mới trở lại. Họ đã đạt được thành công với vị trí thứ ba tại hai kỳ World Cup vào các năm 1974 và 1982. Ba Lan chỉ tham dự Euro lần đầu vào năm 2008 và thành tích tốt nhất của họ là lọt vào tứ kết tại Euro năm 2016.
Thành tích của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Trước khi tìm hiểu về đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 và đánh giá tiềm năng tiến xa của đội tuyển, bạn cần hiểu rõ về thành tích của họ trong vòng loại và những mùa giải trước để có nhận định chính xác nhất.
Hành trình tại vòng loại của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Ba Lan đã thất bại ở bảng E vòng loại Euro 2024, gặp các đối thủ như Albania, CH Séc, Moldova và Quần đảo Faroe. Họ chỉ có được 11 điểm sau 8 trận đấu, bao gồm 3 trận thắng, 2 trận hòa và 3 trận thua. “Đại bàng” Ba Lan xếp thứ ba sau Albania và Cộng hoà Séc.
Điều này cũng có nghĩa là đội phải giành vé qua vòng play-off để tiếp tục tham dự VCK Euro 2024. Trên hành trình gian khổ này, đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 đã giành chiến thắng ấn tượng 5-1 trước Estonia trong trận bán kết và chiến thắng căng thẳng 5-4 trong loạt đá luân lưu với xứ Wales ở trận chung kết.
Thành tích đội tuyển Ba Lan qua các kỳ Euro
Ba Lan đã tham dự 5 vòng chung kết Giải vô địch bóng đá châu Âu, trong đó năm 2012 là đồng chủ nhà (cùng với Ukraina). Thành tích nổi bật nhất là khi họ vào được tứ kết Euro 2016.
Dưới đây là bảng tổng kết thành tích của Ba Lan tại các kỳ Euro:
1960 đến 2004: Không vượt qua vòng loại
Áo – Thụy Sĩ 2008: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Ba Lan – Ukraina 2012: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Pháp 2016: Dừng chân tại Tứ kết
Liên minh châu Âu 2020: Dừng chân tại vòng 1
Đức 2024: Vượt qua vòng loại
Nhìn chung, Ba Lan đã tham dự 5 trong tổng số 17 kỳ Euro, và chỉ một lần vào được tứ kết. Tại Euro 2024, đội tuyển Ba Lan được kỳ vọng sẽ tạo ra thành tích mới cho bóng đá nước nhà.
Kết quả bóng đá EURO
Danh sách các cầu thủ trong đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Dưới đây là danh sách các cầu thủ được chọn vào đội hình của Đội tuyển Bóng đá Quốc gia Ba Lan tham dự Euro 2024. Danh sách đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 bao gồm những cầu thủ có khả năng chiến đấu mạnh mẽ và là niềm hy vọng cho người hâm mộ trong hành trình chinh phục giải đấu lớn này.
Đánh giá về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Bước vào Vòng chung kết Euro 2024, đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 nhận được nhiều kỳ vọng từ người hâm mộ. Bên cạnh đó, họ cũng gặp phải nhiều thách thức và bất lợi tại vòng bảng của mình. Cùng đánh giá về đội với những thông tin sau:
Huấn luyện viên Michal Probierz
Michal Probierz, sinh ngày 24 tháng 9 năm 1972, là một huấn luyện viên bóng đá người Ba Lan và cựu cầu thủ. Ông hiện đang là người phụ trách đội tuyển quốc gia Ba Lan tại giải đấu Euro 2024. Trong sự nghiệp cầu thủ, ông chơi ở vị trí tiền vệ và chủ yếu thi đấu cho Gornik Zabrze.
Với vai trò là huấn luyện viên, ông đã hai lần đoạt Cúp Ba Lan và Siêu cúp Ba Lan, một lần với Jagiellonia Bialystok vào năm 2010 và một lần với Cracovia vào năm 2020. Ông đã dẫn dắt đội U21 Ba Lan vào năm 2022 trước khi chuyển sang dẫn dắt đội tuyển quốc gia Ba Lan vào năm 2023. Sau đó, ông đã dẫn dắt đội tuyển quốc gia giành quyền tham dự UEFA Euro 2024.
Cầu thủ trụ cột của đội Robert Lewandowski
Trong đội hình Ba Lan Euro đã có sự góp mặt của Robert Lewandowski – một trong những tiền đạo hàng đầu tại châu Âu. Hiện tại, cầu thủ này đang thi đấu cho câu lạc bộ Barcelona.
Lewandowski, sinh năm 1988, được coi là một trong những tiền đạo hàng đầu trên thế giới. Anh đang trải qua những năm cuối sự nghiệp và được hy vọng sẽ giúp Ba Lan tiến xa ở giải đấu này.
Bảng đấu của đội tuyển tại VCK Euro 2024
Bảng đấu của đội hình Ba Lan Euro 2024 đã được bốc thăm là Bảng D, bao gồm 4 đội tuyển: Pháp, Hà Lan, Áo và Ba Lan. Pháp được đánh giá là một trong những ứng cử viên hàng đầu cho chức vô địch châu Âu năm nay.
Hà Lan xếp vị trí sau nhưng đội tuyển này có một hàng thủ ấn tượng với nhiều cầu thủ chất lượng. Tuy nhiên, người hâm mộ lo lắng liệu Depay, Gakpo và Weghorst có đủ khả năng ghi bàn để gánh vác nhiệm vụ cho đội bóng hay không.
Nhìn chung, hai đội bóng trên có sự chênh lệch lớn so với các đội còn lại trong bảng D. Tuy nhiên, Áo được đánh giá có phần nhỉnh hơn so với Ba Lan về khả năng đi tiếp nhờ vào màn trình diễn ấn tượng gần đây tại Euro 2024.
Với lịch sử bóng đá lâu đời và sự góp mặt của những cầu thủ kinh nghiệm, Ba Lan với Lewandowski là mối đe dọa đối với hàng thủ của các đội khác. Nhưng thực tế, họ đã có phong độ kém trong vòng loại và cần phải dựa vào may mắn để giành tấm vé đi tiếp ở Vòng chung kết Euro 2024.
Lịch thi đấu của đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024
Lời kết
Với những thông tin được chia sẻ tại euro88.me, hy vọng bạn đã có những thông tin chi tiết về đội hình đội tuyển Ba Lan tại Euro 2024. Tuy chưa có nhiều thành tích ấn tượng tại Euro nhưng đội tuyển Ba Lan vẫn được kỳ vọng sẽ mang đến những trận đấu hấp dẫn cho người hâm mộ bóng đá thế giới.
Tham khảo chi tiết tại: https://euro88.me/doi-hinh-ba-lan-euro-2024/
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Very best late night music radio station, we recommend, AFTERDARK With Odario Williams on CBC radio FM Canada. Fine selection of international sounds sprinkled throughout: https://cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark #AFTERDARK #CBCfm #radio #music #Canada #world #Europe #Asia #Africa #SouthAmerica
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
For the very best in Japanese news, social news and entertainment MIDNIGHT AT THE COFFEE SHOP recommends: TJS Radio. Just click here: https://radio.net/s/tjsradio #Japan #TJSradio #radio #Japan #NorthAmerica #Japanese #Canada #news #entertainmentNews #social
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe