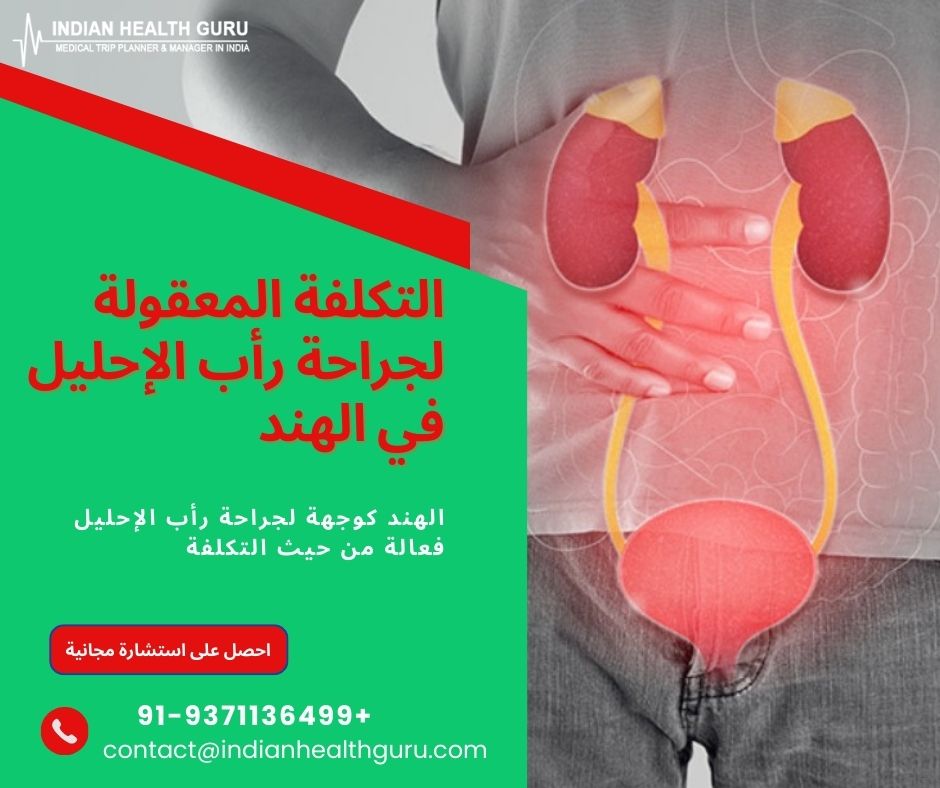
تتضمن عملية رأب الإحليل إعادة بناء مجرى البول لمعالجة مشكلات مثل تضيقات مجرى البول. تختلف أنواع العمليات الجراحية اعتمادًا على موقع التضيق وسببه وطوله.
اتصل بنا:- +91-9371136499
البريد الإلكتروني:- contact@indianhealthguru.com
قراءة المزيد عن: - https://arabrealmedicalexperiences.blogspot.com/2024/07/algeria-affordable-cost-of-urethroplasty-surgery-in-india.html
People
Circles
Posts
We will share the experience of a patient Saahibah Touati from Algeria who sought Cardiac Surgery in India with the help of Indian Health Guru Consultants. We will discuss the cost of surgery, the quality of care, and the overall experience.
#cardiacsurgery #heartsurgery #affordablecost #top10heartsurgeons #besthearthospitals #patientstory #algerianpatient #india
Contact Us:-
☎️ +91-9371136499
📩 contact@indianhealthguru.com
🔗Read More On:- https://successstoriesofglobalpatients.blogspot.com/2024/07/an-algerian-patients-cardiac-surgery-victory-in-india.html
The Turkish Airlines Algiers Office in Algeria offers a wide range of services such as customer support flight information and ticket buying. It is easily accessible in Algiers and attends to the needs of travelers guaranteeing a smooth journey with Turkish Airlines. In order to improve client pleasure the office also helps with specific requests baggage problems and general inquiries.
visit us: https://www.airways-offices.com/turkish-airlines/turkish-airlines-algiers-office/
Videos
The military coup in Niger received considerable media coverage in late July, as the Presidential Guard deposed of Nigerien President Mohamed Bazoum. This coup received significant support from neighboring countries like Burkina Faso, Mali and Guinea, who like Niger, were previously under French colonial influence.
These neighboring countries have since joined a military coalition with Niger, with backing from Algeria, amid growing fears of a potential intervention by the Western-backed states in the ECOWAS coalition. Is a military confronation on the horizon? Or can this be resolved through diplomacy?
The host of The MO Manila Chan sits down with West Africa expert Koffi Kouakou to find the answers to these questions and what the future holds for Niger and the countries of the Sahel.
People
Circles
Videos
The military coup in Niger received considerable media coverage in late July, as the Presidential Guard deposed of Nigerien President Mohamed Bazoum. This coup received significant support from neighboring countries like Burkina Faso, Mali and Guinea, who like Niger, were previously under French colonial influence.
These neighboring countries have since joined a military coalition with Niger, with backing from Algeria, amid growing fears of a potential intervention by the Western-backed states in the ECOWAS coalition. Is a military confronation on the horizon? Or can this be resolved through diplomacy?
The host of The MO Manila Chan sits down with West Africa expert Koffi Kouakou to find the answers to these questions and what the future holds for Niger and the countries of the Sahel.
Posts
تتضمن عملية رأب الإحليل إعادة بناء مجرى البول لمعالجة مشكلات مثل تضيقات مجرى البول. تختلف أنواع العمليات الجراحية اعتمادًا على موقع التضيق وسببه وطوله.
اتصل بنا:- +91-9371136499
البريد الإلكتروني:- contact@indianhealthguru.com
قراءة المزيد عن: - https://arabrealmedicalexperiences.blogspot.com/2024/07/algeria-affordable-cost-of-urethroplasty-surgery-in-india.html
We will share the experience of a patient Saahibah Touati from Algeria who sought Cardiac Surgery in India with the help of Indian Health Guru Consultants. We will discuss the cost of surgery, the quality of care, and the overall experience.
#cardiacsurgery #heartsurgery #affordablecost #top10heartsurgeons #besthearthospitals #patientstory #algerianpatient #india
Contact Us:-
☎️ +91-9371136499
📩 contact@indianhealthguru.com
🔗Read More On:- https://successstoriesofglobalpatients.blogspot.com/2024/07/an-algerian-patients-cardiac-surgery-victory-in-india.html
The Turkish Airlines Algiers Office in Algeria offers a wide range of services such as customer support flight information and ticket buying. It is easily accessible in Algiers and attends to the needs of travelers guaranteeing a smooth journey with Turkish Airlines. In order to improve client pleasure the office also helps with specific requests baggage problems and general inquiries.
visit us: https://www.airways-offices.com/turkish-airlines/turkish-airlines-algiers-office/
Find out why the British Airways Algeria Office is the easiest place to purchase flights, get travel advice, and receive top-notch customer service. Our office guarantees a flawless travel experience with British Airways and is conveniently located in the center of Algeria. Visit us today for all of your travel requirements, and take pleasure in a seamless trip with our committed staff.
Visit Us: https://www.allairlineoffices.com/british-airways/british-airways-algeria-office-in-africa/
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe