Travelers from Kyrgyzstan can access Air Arabia's Bishkek office for easy flight bookings, customer support, and travel information. Because of its central location, it offers easy access to Air Arabia's reasonably priced flights that connect Bishkek to a variety of worldwide destinations. All passengers have smooth travel experiences thanks to the knowledgeable staff. visit us https://www.airlinesofficedetail.com/air-arabia-bishkek-office-in-kyrgyzstan/
People
Circles
Posts
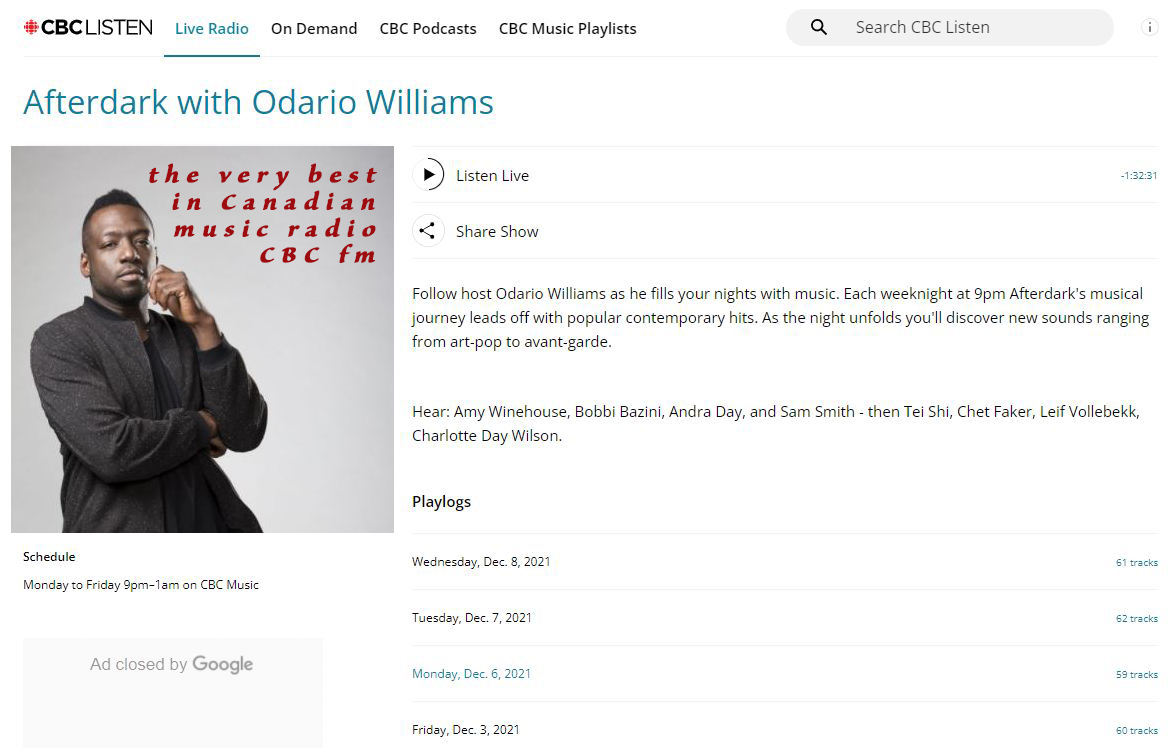
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Videos
People
Circles
Videos
Posts
Travelers from Kyrgyzstan can access Air Arabia's Bishkek office for easy flight bookings, customer support, and travel information. Because of its central location, it offers easy access to Air Arabia's reasonably priced flights that connect Bishkek to a variety of worldwide destinations. All passengers have smooth travel experiences thanks to the knowledgeable staff. visit us https://www.airlinesofficedetail.com/air-arabia-bishkek-office-in-kyrgyzstan/
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Very best late night music radio station, we recommend, AFTERDARK With Odario Williams on CBC radio FM Canada. Fine selection of international sounds sprinkled throughout: https://cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark #AFTERDARK #CBCfm #radio #music #Canada #world #Europe #Asia #Africa #SouthAmerica
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
For the very best in Japanese news, social news and entertainment MIDNIGHT AT THE COFFEE SHOP recommends: TJS Radio. Just click here: https://radio.net/s/tjsradio #Japan #TJSradio #radio #Japan #NorthAmerica #Japanese #Canada #news #entertainmentNews #social
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe