Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee
Introduction
In the world of fashion, some designs capture attention and imagination like no other. The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is a prime example of such creativity. Combining nautical themes with the vibrant aesthetics of Hawaiian shirts, this piece stands out for its bold design and exceptional quality.
About Brixtee
Brixtee is a well-known brand celebrated for its innovative and high-quality apparel. With a reputation for unique and eye-catching designs, Brixtee has carved a niche for itself in the fashion industry. The brand's dedication to creativity and detail is evident in every piece they produce, making their clothing highly desirable for those looking to make a statement.
The Design
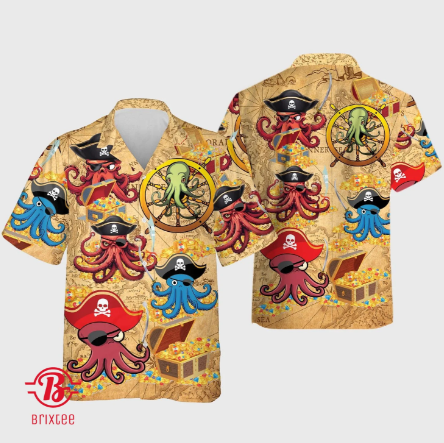
The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt features an intricate and adventurous design. Central to the shirt's appeal is a large octopus, depicted in a pirate theme with a sense of mischief and adventure. The octopus, adorned with pirate hats and accessories, weaves through an oceanic backdrop filled with ships, treasure chests, and waves, creating a dynamic and engaging visual experience.
Material and Comfort
Crafted from top-notch materials, the Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt ensures both comfort and longevity. The lightweight, breathable fabric is perfect for warm climates, making it ideal for summer wear. The shirt's construction reflects Brixtee's commitment to quality, with sturdy stitching and a smooth finish that enhances its overall look and feel.
Versatility
This Hawaiian shirt is remarkably versatile, suitable for various occasions. Whether you're attending a beach gathering, a casual outing, or a themed party, the Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt is sure to draw compliments. Its striking design can be effortlessly paired with shorts, jeans, or swimwear, providing numerous styling options for any event.
Cultural Significance
Hawaiian shirts, also known as Aloha shirts, have a rich cultural heritage, originating from Hawaii in the early 20th century. They were initially made from Japanese kimono fabric and later evolved to incorporate local Hawaiian motifs, symbolizing leisure and the island lifestyle. Brixtee’s modern interpretation of this classic garment combines traditional elements with contemporary flair, honoring the shirt's cultural roots while introducing a fresh perspective.
Conclusion
The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is more than just a garment; it’s a celebration of adventure, creativity, and comfort. With its distinctive design, premium materials, and versatile appeal, this shirt is a must-have for anyone seeking to add a touch of uniqueness and excitement to their wardrobe. Embrace the spirit of the sea and stand out with this exceptional piece from Brixtee.
View product details: https://www.brixtee.com/collections/all-over-print-collection/products/pirates-octopus-hawaiian-shirt
People
Circles
Posts
Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee
Introduction
The fashion world is always evolving, with trends coming and going. However, some pieces remain timeless, capturing the essence of culture and style. The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is one such garment, combining vibrant design, high-quality materials, and a touch of whimsy that appeals to a broad audience.
About Brixtee
Brixtee is a renowned brand known for its unique and creative designs. The company has built a reputation for producing high-quality apparel that stands out in a crowded market. Brixtee’s collections often feature bold graphics, intricate patterns, and a playful approach to fashion, making their pieces highly sought after by trendsetters and fashion enthusiasts alike.
The Design
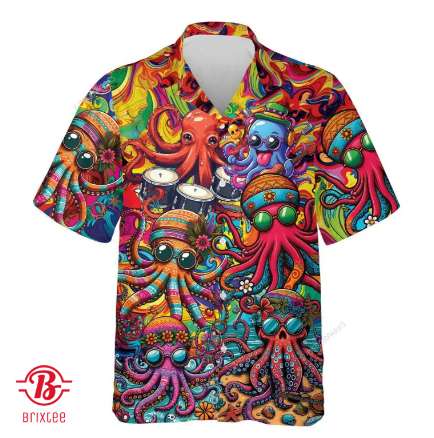
The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt is a testament to Brixtee's commitment to originality and excellence. The shirt features a whimsical octopus design, embodying the carefree and adventurous spirit of the hippie movement. The octopus, adorned with colorful patterns and floral motifs, dances across the fabric, creating a lively and eye-catching aesthetic.
Material and Comfort
Crafted from premium materials, the Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt ensures both comfort and durability. The lightweight fabric is perfect for warm weather, allowing for breathability and ease of movement. The shirt's construction is meticulously done, with attention to detail evident in the stitching and finish.
Versatility
This Hawaiian shirt is incredibly versatile, suitable for a variety of occasions. Whether you're heading to a beach party, a casual outing, or a summer festival, the Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt is sure to make a statement. Its vibrant design can be paired with shorts, jeans, or even swimwear, offering endless styling possibilities.
Cultural Significance
Hawaiian shirts, also known as Aloha shirts, have a rich cultural history. Originating in Hawaii in the early 20th century, these shirts were initially made from Japanese kimono fabric and later incorporated local Hawaiian motifs. They symbolize relaxation, leisure, and the island lifestyle. Brixtee’s modern take on this classic garment pays homage to its origins while infusing contemporary elements.
Conclusion
The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is more than just a piece of clothing; it’s a celebration of culture, creativity, and comfort. With its vibrant design, high-quality materials, and versatile nature, this shirt is a must-have for anyone looking to add a touch of whimsy and style to their wardrobe. Embrace the spirit of aloha and stand out from the crowd with this unique piece from Brixtee.
View product details: https://www.brixtee.com/collections/all-over-print-collection/products/hippie-octopus-aloha-hawaiian-shirt
Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding: A Fusion of Tradition and Modernity
In the ever-evolving world of fashion, certain designs stand out by seamlessly blending traditional elements with contemporary style. The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is one such remarkable creation. Known for its innovative and high-quality designs, Skillridding has crafted a shirt that captures the essence of cultural heritage while appealing to modern fashion sensibilities.
Elegant Design
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt is distinguished by its elegant and sophisticated design. It features traditional Japanese motifs and calligraphy, artfully integrated into a modern shirt silhouette. The intricate patterns and symbols pay homage to Japanese culture, creating a unique and visually striking garment. The shirt's design is not only aesthetically pleasing but also carries a sense of history and cultural significance.
Premium Fabric Quality
Skillridding is renowned for its use of premium materials, and the Yamamoto Sign Shirt is a testament to this commitment. Made from high-quality, breathable fabric, the shirt offers exceptional comfort and durability. The material is soft to the touch and lightweight, making it suitable for various occasions, from casual outings to more formal events. The shirt's fabric ensures that it retains its shape and vibrant colors even after repeated washes, guaranteeing long-lasting wear.
Versatility and Style
One of the standout features of the Yamamoto Sign Shirt is its versatility. Its design makes it suitable for a wide range of occasions, allowing wearers to dress it up or down according to the event. Pair it with tailored trousers for a sophisticated look at a formal gathering, or with jeans for a stylish yet casual ensemble. The shirt's unique design and high-quality fabric make it a versatile addition to any wardrobe, offering endless styling possibilities.
Attention to Detail
Skillridding's attention to detail is evident in every aspect of the Yamamoto Sign Shirt. From the precise stitching to the carefully crafted buttons, each element is meticulously designed to ensure a high-quality product. The shirt's fit is tailored to provide comfort while enhancing the wearer's silhouette. The finishing touches, such as the subtle embroidery and the choice of colors, reflect Skillridding's dedication to creating garments that are both stylish and refined.
Embracing Cultural Heritage
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is more than just a piece of clothing; it is a celebration of cultural heritage. By incorporating traditional Japanese elements into a contemporary design, the shirt allows wearers to connect with and appreciate Japanese culture. It serves as a reminder of the rich history and artistic traditions that continue to inspire modern fashion.
Conclusion
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is a perfect blend of tradition and modernity. Its elegant design, premium fabric quality, and versatility make it a must-have for anyone looking to add a touch of sophistication and cultural richness to their wardrobe. Whether you are attending a formal event or enjoying a casual day out, this shirt offers a stylish and meaningful way to express your appreciation for Japanese culture. Embrace the fusion of tradition and contemporary style with the Yamamoto Sign Shirt, and make a lasting impression with this exceptional piece from Skillridding.
View product details: https://www.skullridding.com/collections/featured-collection/products/yamamoto-sign-shirt
Videos
On this episode of The M.O., host Manila Chan dives into the hot topic of the re-militarization of Japan. Manila sits down with author James Bradley to discuss Japanese history after World War II and the subsequent move by Tokyo to boost their military budget in the face of a perceived Chinese and North Korean threat.
Descendants of slaves, the Polish government, and native Americans who were sterilized by the state are just a few of the different groups around the world who are demanding reparations for past injustices against their ancestors. On this addition of 360 View, international correspondent Roxana Solano looks back at how reparations have been used throughout history. Then, host Scottie Nell Hughes discusses with American historian, Gerald Horne, which groups around the world are asking for reparations and what countries are making plans to pay them.
In the wake of the Silicon Valley Bank ordeal, Dr. Peter Onge delivered this insightful video surrounding the question as to whether or not the FDIC bailout is, in fact, a "bailout" in the traditional sense of the term.
St Onge is a Research Fellow in the Thomas A. Roe Institute for Economic Policy Studies and the Mark A. Kolokotrones Fellow in Economic Freedom at The Heritage Foundation. He holds a Ph.D. in Economics from George Mason University, and a B.A. in Economics and Political Science from McGill University.
Before joining the Heritage Foundation, Peter was a fellow at the Mises Institute, a senior fellow at the Montreal Economic Institute, and an assistant professor of International Trade and of Marketing at Taiwan’s Feng Chia University. Before academia, he held senior strategy and marketing positions at Harris Corporation of Florida and Takara Toys, Ltd. of Japan. He has lived extensively in Mexico, Brazil, Canada, Japan, and Taiwan, and speaks fluent Spanish, French, Japanese, and is conversational in Mandarin.
People
Circles
Videos
On this episode of The M.O., host Manila Chan dives into the hot topic of the re-militarization of Japan. Manila sits down with author James Bradley to discuss Japanese history after World War II and the subsequent move by Tokyo to boost their military budget in the face of a perceived Chinese and North Korean threat.
Descendants of slaves, the Polish government, and native Americans who were sterilized by the state are just a few of the different groups around the world who are demanding reparations for past injustices against their ancestors. On this addition of 360 View, international correspondent Roxana Solano looks back at how reparations have been used throughout history. Then, host Scottie Nell Hughes discusses with American historian, Gerald Horne, which groups around the world are asking for reparations and what countries are making plans to pay them.
In the wake of the Silicon Valley Bank ordeal, Dr. Peter Onge delivered this insightful video surrounding the question as to whether or not the FDIC bailout is, in fact, a "bailout" in the traditional sense of the term.
St Onge is a Research Fellow in the Thomas A. Roe Institute for Economic Policy Studies and the Mark A. Kolokotrones Fellow in Economic Freedom at The Heritage Foundation. He holds a Ph.D. in Economics from George Mason University, and a B.A. in Economics and Political Science from McGill University.
Before joining the Heritage Foundation, Peter was a fellow at the Mises Institute, a senior fellow at the Montreal Economic Institute, and an assistant professor of International Trade and of Marketing at Taiwan’s Feng Chia University. Before academia, he held senior strategy and marketing positions at Harris Corporation of Florida and Takara Toys, Ltd. of Japan. He has lived extensively in Mexico, Brazil, Canada, Japan, and Taiwan, and speaks fluent Spanish, French, Japanese, and is conversational in Mandarin.
Posts
Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee
Introduction
In the world of fashion, some designs capture attention and imagination like no other. The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is a prime example of such creativity. Combining nautical themes with the vibrant aesthetics of Hawaiian shirts, this piece stands out for its bold design and exceptional quality.
About Brixtee
Brixtee is a well-known brand celebrated for its innovative and high-quality apparel. With a reputation for unique and eye-catching designs, Brixtee has carved a niche for itself in the fashion industry. The brand's dedication to creativity and detail is evident in every piece they produce, making their clothing highly desirable for those looking to make a statement.
The Design
The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt features an intricate and adventurous design. Central to the shirt's appeal is a large octopus, depicted in a pirate theme with a sense of mischief and adventure. The octopus, adorned with pirate hats and accessories, weaves through an oceanic backdrop filled with ships, treasure chests, and waves, creating a dynamic and engaging visual experience.
Material and Comfort
Crafted from top-notch materials, the Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt ensures both comfort and longevity. The lightweight, breathable fabric is perfect for warm climates, making it ideal for summer wear. The shirt's construction reflects Brixtee's commitment to quality, with sturdy stitching and a smooth finish that enhances its overall look and feel.
Versatility
This Hawaiian shirt is remarkably versatile, suitable for various occasions. Whether you're attending a beach gathering, a casual outing, or a themed party, the Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt is sure to draw compliments. Its striking design can be effortlessly paired with shorts, jeans, or swimwear, providing numerous styling options for any event.
Cultural Significance
Hawaiian shirts, also known as Aloha shirts, have a rich cultural heritage, originating from Hawaii in the early 20th century. They were initially made from Japanese kimono fabric and later evolved to incorporate local Hawaiian motifs, symbolizing leisure and the island lifestyle. Brixtee’s modern interpretation of this classic garment combines traditional elements with contemporary flair, honoring the shirt's cultural roots while introducing a fresh perspective.
Conclusion
The Pirates Octopus Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is more than just a garment; it’s a celebration of adventure, creativity, and comfort. With its distinctive design, premium materials, and versatile appeal, this shirt is a must-have for anyone seeking to add a touch of uniqueness and excitement to their wardrobe. Embrace the spirit of the sea and stand out with this exceptional piece from Brixtee.
View product details: https://www.brixtee.com/collections/all-over-print-collection/products/pirates-octopus-hawaiian-shirt
Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee
Introduction
The fashion world is always evolving, with trends coming and going. However, some pieces remain timeless, capturing the essence of culture and style. The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is one such garment, combining vibrant design, high-quality materials, and a touch of whimsy that appeals to a broad audience.
About Brixtee
Brixtee is a renowned brand known for its unique and creative designs. The company has built a reputation for producing high-quality apparel that stands out in a crowded market. Brixtee’s collections often feature bold graphics, intricate patterns, and a playful approach to fashion, making their pieces highly sought after by trendsetters and fashion enthusiasts alike.
The Design
The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt is a testament to Brixtee's commitment to originality and excellence. The shirt features a whimsical octopus design, embodying the carefree and adventurous spirit of the hippie movement. The octopus, adorned with colorful patterns and floral motifs, dances across the fabric, creating a lively and eye-catching aesthetic.
Material and Comfort
Crafted from premium materials, the Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt ensures both comfort and durability. The lightweight fabric is perfect for warm weather, allowing for breathability and ease of movement. The shirt's construction is meticulously done, with attention to detail evident in the stitching and finish.
Versatility
This Hawaiian shirt is incredibly versatile, suitable for a variety of occasions. Whether you're heading to a beach party, a casual outing, or a summer festival, the Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt is sure to make a statement. Its vibrant design can be paired with shorts, jeans, or even swimwear, offering endless styling possibilities.
Cultural Significance
Hawaiian shirts, also known as Aloha shirts, have a rich cultural history. Originating in Hawaii in the early 20th century, these shirts were initially made from Japanese kimono fabric and later incorporated local Hawaiian motifs. They symbolize relaxation, leisure, and the island lifestyle. Brixtee’s modern take on this classic garment pays homage to its origins while infusing contemporary elements.
Conclusion
The Hippie Octopus Aloha Hawaiian Shirt by Brixtee is more than just a piece of clothing; it’s a celebration of culture, creativity, and comfort. With its vibrant design, high-quality materials, and versatile nature, this shirt is a must-have for anyone looking to add a touch of whimsy and style to their wardrobe. Embrace the spirit of aloha and stand out from the crowd with this unique piece from Brixtee.
View product details: https://www.brixtee.com/collections/all-over-print-collection/products/hippie-octopus-aloha-hawaiian-shirt
Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding: A Fusion of Tradition and Modernity
In the ever-evolving world of fashion, certain designs stand out by seamlessly blending traditional elements with contemporary style. The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is one such remarkable creation. Known for its innovative and high-quality designs, Skillridding has crafted a shirt that captures the essence of cultural heritage while appealing to modern fashion sensibilities.
Elegant Design
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt is distinguished by its elegant and sophisticated design. It features traditional Japanese motifs and calligraphy, artfully integrated into a modern shirt silhouette. The intricate patterns and symbols pay homage to Japanese culture, creating a unique and visually striking garment. The shirt's design is not only aesthetically pleasing but also carries a sense of history and cultural significance.
Premium Fabric Quality
Skillridding is renowned for its use of premium materials, and the Yamamoto Sign Shirt is a testament to this commitment. Made from high-quality, breathable fabric, the shirt offers exceptional comfort and durability. The material is soft to the touch and lightweight, making it suitable for various occasions, from casual outings to more formal events. The shirt's fabric ensures that it retains its shape and vibrant colors even after repeated washes, guaranteeing long-lasting wear.
Versatility and Style
One of the standout features of the Yamamoto Sign Shirt is its versatility. Its design makes it suitable for a wide range of occasions, allowing wearers to dress it up or down according to the event. Pair it with tailored trousers for a sophisticated look at a formal gathering, or with jeans for a stylish yet casual ensemble. The shirt's unique design and high-quality fabric make it a versatile addition to any wardrobe, offering endless styling possibilities.
Attention to Detail
Skillridding's attention to detail is evident in every aspect of the Yamamoto Sign Shirt. From the precise stitching to the carefully crafted buttons, each element is meticulously designed to ensure a high-quality product. The shirt's fit is tailored to provide comfort while enhancing the wearer's silhouette. The finishing touches, such as the subtle embroidery and the choice of colors, reflect Skillridding's dedication to creating garments that are both stylish and refined.
Embracing Cultural Heritage
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is more than just a piece of clothing; it is a celebration of cultural heritage. By incorporating traditional Japanese elements into a contemporary design, the shirt allows wearers to connect with and appreciate Japanese culture. It serves as a reminder of the rich history and artistic traditions that continue to inspire modern fashion.
Conclusion
The Yamamoto Sign Shirt by Skillridding is a perfect blend of tradition and modernity. Its elegant design, premium fabric quality, and versatility make it a must-have for anyone looking to add a touch of sophistication and cultural richness to their wardrobe. Whether you are attending a formal event or enjoying a casual day out, this shirt offers a stylish and meaningful way to express your appreciation for Japanese culture. Embrace the fusion of tradition and contemporary style with the Yamamoto Sign Shirt, and make a lasting impression with this exceptional piece from Skillridding.
View product details: https://www.skullridding.com/collections/featured-collection/products/yamamoto-sign-shirt
🚨 Japanese Doctors Confirm Rare Heart Condition After COVID Shot
A case study from Japan has documented the first known biopsy-proven instance of inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy (iDCM) — a condition where the heart becomes enlarged and weakened due to inflammation — following COVID-19 vaccination.
⬇️
https://childrenshealthdefense.org/defender/cardiomyopathy-covid-vaccines-japan-study/?utm_source=sovren&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=defender&utm_id=20240723

Doctors in Japan who documented the first known biopsy-proven instance of inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy — a condition where the heart becomes enlarged and weakened due to inflammation — following COVID-19 vaccination said their case study demonstrates the value of advanced diagnostic techniques in identifying and understanding vaccine-related side effects.
childrenshealthdefense.org
日本語 ChatGPT 2024: 革新的なAI対話システムの新基準
日本語 ChatGPT 2024 は、その先進的な機能と使いやすさで、AI対話システムの最前線に立っています。この革新的なプラットフォームは、多彩なユニークな機能、美しいインターフェース、そして非常に迅速な応答能力によって、ユーザーに革新的な体験を提供します。
私たちの知識をあなたと共有してください: https://chatgptjapanese.net/
多彩なユニークな機能
日本語 ChatGPT 2024 の特筆すべき機能の一つは、その多彩さです。システムは単なる質問に答えるだけでなく、複雑なタスクの実行や専門知識の提供にも対応します。医療、法律、技術などの領域で高度なアドバイスや情報を即座に提供し、ユーザーのニーズに応じたカスタマイズされたサービスを提供します。
美しいインターフェース
日本語 ChatGPT 2024 のインターフェースは、その美しさと使いやすさでユーザーを魅了します。直感的なデザインと洗練されたレイアウトにより、初めて利用するユーザーでもストレスなくシステムを操作できます。情報の整理や視覚的な表現も優れており、ユーザーは迷うことなく目的の情報にアクセスできます。
いつでもどこでもアクセス可能
このシステムは、どこからでも簡単にアクセスできる点でも注目に値します。スマートフォン、タブレット、パソコンなど、さまざまなデバイスを通じて利用可能であり、ユーザーは自宅、オフィス、移動中など、場所を選ばずにAIとの対話を維持できます。インターネット接続さえあれば、24時間365日いつでも利用可能であり、迅速な情報収集や問題解決をサポートします。
非常に迅速な応答能力
最後に、日本語 ChatGPT 2024 のもう一つの魅力はその非常に迅速な応答能力です。システムは最新の自然言語処理技術を駆使し、リアルタイムでユーザーの入力に対応します。これにより、会話の流れを途切れさせることなく、自然でスムーズな対話を実現します。ユーザーは即座に情報を得ることができ、迅速な意思決定や問題解決が可能です。
結論
日本語 ChatGPT 2024 は、その革新的な機能、美しいインターフェース、どこでもアクセス可能な性質、そして非常に迅速な応答能力によって、次世代のAI対話システムの基準を確立しました。これにより、個人の日常生活からビジネスの現場まで、幅広い分野で革新的な利用が期待されます。
接触
会社名:ChatGPT Japanese - ChatGPT 日本語
市区町村:東京都渋谷区
国: 日本
郵便番号:150-0022
電話番号:+81 80-1234-5678
メール:chatgptjapanese@gmail.com
Google Map:東京都渋谷区恵比寿南1-2-3
#日本語チャットgpt,#日本語チャットgpt,#無料チャットgpt