👨⚕💉💊🩺 Le Dr P. Jagannath India est spécialisé dans les traitements oncologiques de pointe et la médecine personnalisée, en se concentrant sur le bien-être holistique de l'esprit, du corps et de l'âme de chaque patient. P. Jagannath, meilleur oncologue de Mumbai, reconnaît que dans de nombreux cas de cancers à un stade avancé, la guérison peut ne pas être réalisable. 👨⚕💉💊🩺
📌Pour plus d'informations, vous pouvez nous contacter :-
✅Contact:- +91 9371770341
✅Site Web : - www.indiacancersurgerysite.com
✅Identifiant de courrier électronique : - dr.pjagannath@indiacancersurgerysite.com
👉 Lire la suite :- https://french-health-trip-2-india.blogspot.com/2024/07/chad-dr-p-jagannaths-comprehensive-oncology-care-in-mumbai.html
People
Circles
Posts
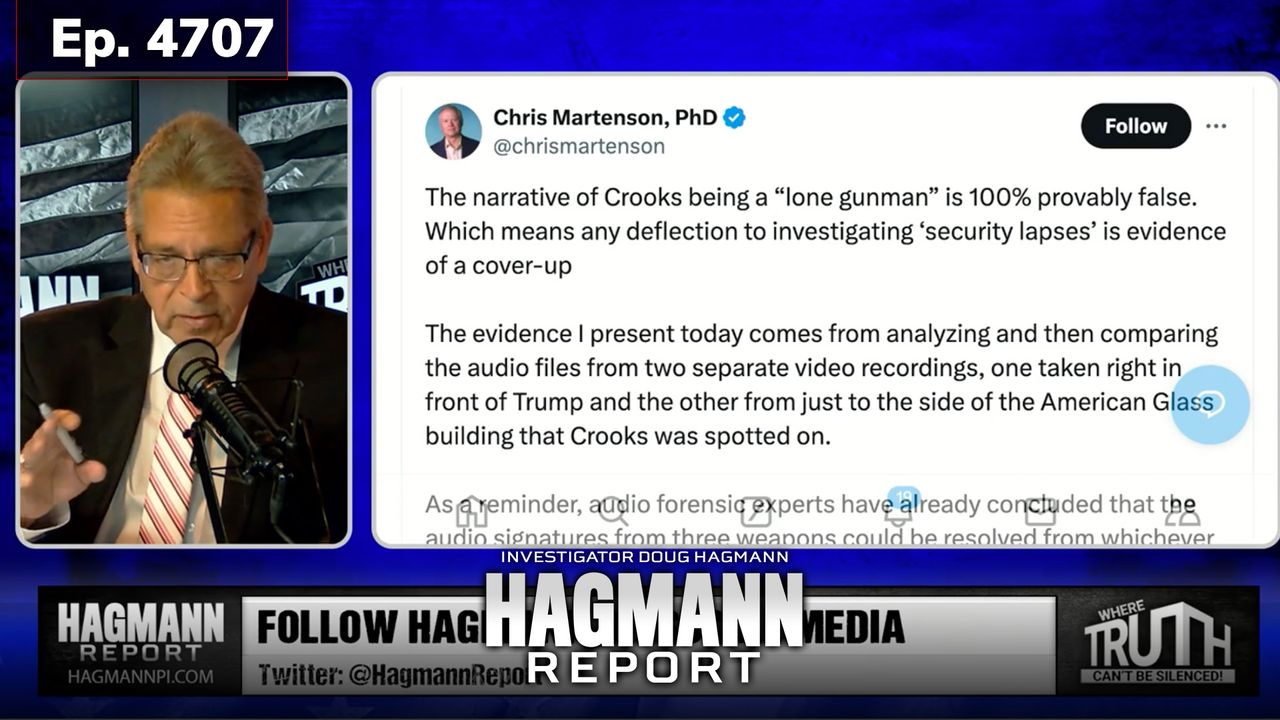
Ep 4707: Multiple Deep-State Coup Plots Exposed & It's Far From Over | Chad R. Stewart Joins Doug Hagmann | July 22, 2024
https://www.brighteon.com/763ffa26-4228-4500-84da-442164684ec7
Nature’s Morphine? Medical scientist Clint Winters discusses the incredible pain relief effects of 100% Drug-Free Conolidine. This changes pain relief: https://trycono.com/Hagmann --------------------------------------------PLEASE SUBSCRIBE to our channels on Rumble & Brighteon, and give us a “Like,” and PLEASE share this episode and this channel on your social media feed, and THANK YOU for your support!----------------------SPECIAL: This stuff works better than ANYTHING I've used! Nana Soma - https://iwantmyhealthback.com/hagmann - PLEASE click & check it out at the link. You'll thank me later.----------------------For complete information, please visit, bookmark, and share The Hagmann Report at our website:https://www.HagmannPI.comTIPS: (Anonymity guaranteed): doug@hagmannreport.com. | rt@hhagmannpi.comON THE GO? SUBSCRIBE TO HAGMANN’S PODCAST:iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/hagmann-report/id631558915?uo=4Spotify: BANNED!iHeart: https://www.iheart.com/podcast/256-hagmann-report-30926499/ Spreaker: https://www.spreaker.com/show/hagmann-report FOLLOW HAGMANN AT:Twitter: https://twitter.com/HagmannReportGab: https://gab.com/DougHagmann Gettr: https://gettr.com/user/doughagmann Truth Social: https://truthsocial.com/@DougHagmann
www.brighteon.com
👨⚕💉💊🩺 L'Inde propose une large gamme d'hôpitaux de transplantation de moelle osseuse économiques, répondant à différents besoins financiers. Avec les progrès dans le domaine médical, ces hôpitaux s'efforcent de rendre les traitements plus abordables et accessibles à tous. 👨⚕💉💊🩺
📌Pour plus d'informations, vous pouvez nous contacter :-
✅Contact:- +91 9765025331
✅Site Web : - www.indiaorgantransplant.com/
✅Identifiant de courrier électronique :-info@indiaorgantransplant.com
👉 Lire la suite : - https://french-health-trip-2-india.blogspot.com/2024/07/chad-budget-friendly-bone-marrow-transplant-hospitals-in-india.html
Videos
Circles
Videos
Posts
👨⚕💉💊🩺 Le Dr P. Jagannath India est spécialisé dans les traitements oncologiques de pointe et la médecine personnalisée, en se concentrant sur le bien-être holistique de l'esprit, du corps et de l'âme de chaque patient. P. Jagannath, meilleur oncologue de Mumbai, reconnaît que dans de nombreux cas de cancers à un stade avancé, la guérison peut ne pas être réalisable. 👨⚕💉💊🩺
📌Pour plus d'informations, vous pouvez nous contacter :-
✅Contact:- +91 9371770341
✅Site Web : - www.indiacancersurgerysite.com
✅Identifiant de courrier électronique : - dr.pjagannath@indiacancersurgerysite.com
👉 Lire la suite :- https://french-health-trip-2-india.blogspot.com/2024/07/chad-dr-p-jagannaths-comprehensive-oncology-care-in-mumbai.html
Ep 4707: Multiple Deep-State Coup Plots Exposed & It's Far From Over | Chad R. Stewart Joins Doug Hagmann | July 22, 2024
https://www.brighteon.com/763ffa26-4228-4500-84da-442164684ec7

Nature’s Morphine? Medical scientist Clint Winters discusses the incredible pain relief effects of 100% Drug-Free Conolidine. This changes pain relief: https://trycono.com/Hagmann --------------------------------------------PLEASE SUBSCRIBE to our channels on Rumble & Brighteon, and give us a “Like,” and PLEASE share this episode and this channel on your social media feed, and THANK YOU for your support!----------------------SPECIAL: This stuff works better than ANYTHING I've used! Nana Soma - https://iwantmyhealthback.com/hagmann - PLEASE click & check it out at the link. You'll thank me later.----------------------For complete information, please visit, bookmark, and share The Hagmann Report at our website:https://www.HagmannPI.comTIPS: (Anonymity guaranteed): doug@hagmannreport.com. | rt@hhagmannpi.comON THE GO? SUBSCRIBE TO HAGMANN’S PODCAST:iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast/hagmann-report/id631558915?uo=4Spotify: BANNED!iHeart: https://www.iheart.com/podcast/256-hagmann-report-30926499/ Spreaker: https://www.spreaker.com/show/hagmann-report FOLLOW HAGMANN AT:Twitter: https://twitter.com/HagmannReportGab: https://gab.com/DougHagmann Gettr: https://gettr.com/user/doughagmann Truth Social: https://truthsocial.com/@DougHagmann
www.brighteon.com
👨⚕💉💊🩺 L'Inde propose une large gamme d'hôpitaux de transplantation de moelle osseuse économiques, répondant à différents besoins financiers. Avec les progrès dans le domaine médical, ces hôpitaux s'efforcent de rendre les traitements plus abordables et accessibles à tous. 👨⚕💉💊🩺
📌Pour plus d'informations, vous pouvez nous contacter :-
✅Contact:- +91 9765025331
✅Site Web : - www.indiaorgantransplant.com/
✅Identifiant de courrier électronique :-info@indiaorgantransplant.com
👉 Lire la suite : - https://french-health-trip-2-india.blogspot.com/2024/07/chad-budget-friendly-bone-marrow-transplant-hospitals-in-india.html
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe









