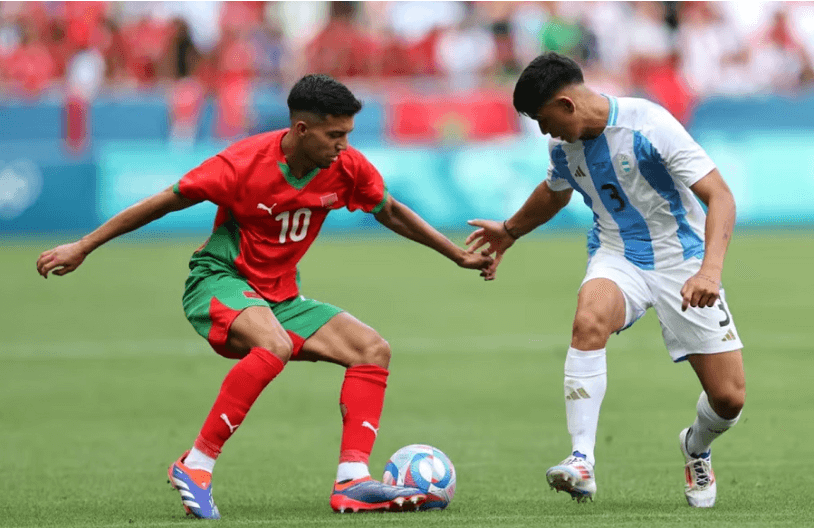
Argentina bị fan cáo buộc được ‘dàn xếp trắng trợn’
Trận ra quân của U23 Argentina trước U23 Morocco tại Olympic Paris 2024 đã tạo ra tranh cãi dữ dội.
Khi trận đấu bước sang phút 90, thời điểm Argentina đang bị Morocco dẫn 2-1, trọng tài bàn Frida Klarlund giơ biển thông báo sẽ có đến 15 phút bù giờ hiệp 2.
#https://syrum-game.com/tin-tuc/argentina-bi-fan-cao-buoc-duoc-dan-xep-trang-tron/
Circles
Posts
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Videos
Circles
Videos
Posts
Argentina bị fan cáo buộc được ‘dàn xếp trắng trợn’
Trận ra quân của U23 Argentina trước U23 Morocco tại Olympic Paris 2024 đã tạo ra tranh cãi dữ dội.
Khi trận đấu bước sang phút 90, thời điểm Argentina đang bị Morocco dẫn 2-1, trọng tài bàn Frida Klarlund giơ biển thông báo sẽ có đến 15 phút bù giờ hiệp 2.
#https://syrum-game.com/tin-tuc/argentina-bi-fan-cao-buoc-duoc-dan-xep-trang-tron/
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe