International Public Notice: The Bear in the China Shop
By Anna Von Reitz
The following brief case commentary from the United States Supreme Court (the Federal Republic Court in 1805) comes from a Law Memorandum written by the immortal John Trowbridge in which he is at pains to explain the difference between confederate states (States of America) operating the Federal Republic under The Constitution for the united States of America and the District States created by General Washington as administrative units of the Territorial District of Columbia Government and all of these "states" versus the Territories and Possessions of the United States known as the "Insular States":
"The Supreme Court explains the political distinction between, on the one hand, the members of
the Union, and on the other, the District of Columbia and the territories:
"On the part of the plaintiffs, it has been urged that Columbia is a distinct political society, and is therefore “a state” according to the definitions of writers on general law.
This is true. But as the act of Congress obviously uses the word “state” in reference to the term as used in the Constitution, it becomes necessary to inquire whether Columbia is a state in the sense of that instrument.
The result of that examination is a conviction that
the members of the American confederacy only are the states contemplated in the Constitution.
. . . These clauses show that the word “state” is used in the Constitution as designating a member of the union [of the original Confederation doing business as the States of America], and excludes from the term the signification attached to it by writers on the law of nations."
[Underline and boldface emphasis added.] Hepburn & Dundas v. Ellzey, 6 U.S. 445, 452, 2 Cranch 445, 2 L.Ed. 332 (1805).
"It has been attempted to distinguish a Territory from the district [sic] of Columbia; but the court is of opinion that this distinction cannot be maintained.
They may differ in many respects, but neither of them is a state, in the sense in which that term is used in the constitution."
[Emphasis added.] New Orleans v. Winter, 1 Wheat. (U. S.) 91, 4 L. Ed. 44 (1816).
These are definitive findings of the actual Federal Republic Supreme Court having the proper jurisdiction to decide these issues and what we herein discover is that:
The various kinds of "territories" either created administratively by the district of Columbia or arising as natural properties (Insular States) are not the "states" referenced in the Constitution.
The "states" in the Constitution being referenced in 1805 are the Confederate states, that is "states of state" that were members of the American Confederation formed in 1781 and known as "the American Confederacy" long before Jefferson Davis was born.
This all makes sense, as the American States of States were the members of the States of America -- that is, the Confederation -- awarded the Federal Constitution known as "The Constitution for the united States of America" in 1787.
Secondly, neither the district of Columbia nor the Territories attached to it are "states" of this kind.
As we put it in our second International Public Notice addressed to Derek Johnson, George Washington created District States, not state districts; the government of the district called "Columbia" is distinct and its "states" are distinct both from the Confederate states and the United States Territories, even though all three might meet the definition of "state" contemplated more generally under international law.
These two Supreme Court cases tell us that within the purview of the Constitution forming the Federal Republic the only "states" contemplated are the members of the original American Confederacy.
This distinction explains how we have (1) an American Federal Subcontractor, dba, States of America, and its states which are members of the American Confederacy, and (2) a district of Columbia Subcontractor and its territories (District States) which are not "states" within the meaning of the Federal Constitution, and (3) separate United States Territories and Possessions which are not "states" in this context, either.
Now you can better contemplate the complexity of the original Federal Government structure and discern how the use of the word "state" was contextually used to mean some states and not others.
For Constitutional purposes, the word "state" refers to the Confederate states belonging to the "States of America", the doing-business-as name of the original Confederation formed in 1781 which was awarded The Constitution for the united States of America in 1787. This is the Federal Government known as the Federal Republic.
In the original Federal Constitution (1787), the word "state" does not refer to the District States set up by George Washington to administer the district of Columbia and its territories (1789 Constitution), nor does it refer to the United States Territories and Possessions as "states" (1790 Constitution).
To summarize:
(1) We have the Union States that occupy the national soil jurisdiction of each nation-state.
(2) We have the Federation States that occupy the international land and sea jurisdiction belonging to each nation-state, and the members of the Federation, called States of the Union.
(3) We had the Confederate States (States-of-States) that were members of the original 1781 Confederation that occupied the global air jurisdiction belonging to each nation-state, and which were known jointly as "the American Confederacy".
(4) We had the above-mentioned Confederation doing business as the States of America and operating the Federal Republic under the 1787 Constitution for the united States of America until 1861 when the American Confederacy lost the necessary quorum to conduct business; at which point, the individual "Federal Republics" operated as another form of "states" also failed.
(5) We still have the District States arising under the Northwest Ordinance and territories of the district of Columbia, sometimes called "Federal enclaves", or Federal Management Units, Judicial Districts, Military Districts, etc.
(6) We still have the United States Territories and Possessions, sometimes called "the Insular States".
All of six of these governmental entities, three American and three Federal, have given rise to "states" and it behooves us to know this and to know that the general meaning of "states" accepted by the Law of Nations is not used in Federal Codes and documents; since early on, each document or Act of Congress defines the word "state" as a legal term for the purposes of that document, treaty, or code.
You can now see why this is necessary.
Our Union States and our States of the Union have never stood under any Constitution.
The American Federation of States that the "Federal Government" is named after, delegated the "enumerated powers" to the Federal Subcontractors.
The Federation could never stand under any Constitution as a result of this role, and neither could its member States.
The only form of American "State" to subject themselves and their Confederation to service under a Constitution were the original Confederate States of America (1781 to 1861) and these were all "States of States" -- separate organizations in the business of providing governmental services under contract.
None of these above referenced "states" known as the Union States or as the States of the Union nor as the original Confederate States were of any Territorial origin. They were (in the case of the Confederacy) or are (in the case of the Union States and Federation States) of uniquely American origin.
The District (that is, Territorial) States are a different story and arise on paper as a result of duties owed by the British Territorial Subcontractors under the Northwest Ordinance.
Likewise, the so-called Insular States, Puerto Rico, Guam, American Samoa, et alia, are known as territorial states and possessions of the United States.
All this tangled history, all these various kinds of "states" -- both those currently existing and those that are "missing" and awaiting reconstruction -- have to be separately known and acknowledged and defined, their powers and relationships accounted for, or it is literally impossible to know what you mean by "United States" or "States of America" or "United States of America".
The later incorporation of the British Territorial version of "the United States of America" to create "the United States of America -- Incorporated" added another layer of complexity, as we must additionally distinguish between incorporated and unincorporated "states".
Still later, the Municipal Government of the United States also incorporated Municipal Corporations named after our States, distinguished as STATES, which are foreign Municipal Corporations.
These additional incorporated "states" and "states of states" just muddy the water more and cause more confusion and these are business entities only, arising on paper; they are owned and operated by the Federal Subcontractors, not the American people.
Bottom line: we have been feloniously impersonated and so have our States of the Union.
We have been "assumed" to be responsible for the debts and outrages of these foreign corporations and their "states", without our knowledge or consent.
We have been "presumed to acquiesce" to their activities apportioning themselves new rights, new roles, and new empowerments, including but not limited to more than fifteen unilateral and unratified (by our States) Amendments to their service contracts, and endless drafts against our credit, and the unregulated enforcement of vast quantities of new Federal Code, representing impositions that were never granted to them via any contract.
Let it be known that these Subcontractors never consulted nor fully informed their employers of their actions and presumptions and never bothered to actually implement the remedies published as a means to legalize their theft of American property.
This leads to the inevitable conclusion that these foreign Employees working as Federal Subcontractors, used the plethora of confusions related to the kind and nature of "states", and the absence of the American Confederacy after the Civil War, to promote a mammoth and secretive fraud scheme against their actual Employers.
The absence of the American Confederacy in no way excuses their obligations owed to the American People and to the States of the Union and the Union States.
The absence of the American Confederacy doesn't grant them any additional contracts or special powers. It doesn't elevate or change the nature of their "states". It doesn't ratify all the unratified "Amendments" they have unilaterally made to their own service contracts. It doesn't allow them to declare war. It doesn't allow them to impersonate Americans as "Federal Citizens" via undisclosed and unconscionable registrations and enrollments and enlistments. It doesn't allow them to impersonate our Federation of States as a foreign incorporated entity.
The American Confederacy was never their Employer, and its duties were never vouchsafed to them.
Their gross failure to fully inform the Federation of States that delegated their "powers" to them, and their subsequent criminal activities resulting in gross harm to their employers speak for themselves.
These "Federal Corporations" have been operating as rogue "states" -- and they are not "states" of ours.
We have only by dint of our own hard work and investigation determined what these foreign entities have done "in our names" and falsely alleged against our country and our people. No disclosure was provided to us or to our States of the Union by these criminal miscreants, who are the responsibility of the Pope and His Imperial Majesty, "King" Charles, and the Lord Mayor of London.
There is no contract or agreement allowing our Federal Subcontractors to promote a Mercenary Conflict on our shores and the continuation of this illegal and immoral nonsense for 164 years in view of the fact that both these organizations are ultimately owned and operated by the Pope -- directly in the case of the Municipal Corporations, and indirectly through his Commonwealth Overseer in the case of the Territorial Corporations --- is purely criminal.
The Popes and the British Monarchs and the Governors and Mayors of Westminster have owed us good faith service throughout the duration of this self-interested crime spree, and they have fraudulently pretended to be our protectors, allies, and custodians throughout this criminal rampage of predation and impersonation, racketeering, human trafficking, and political usurpation.
The shame and the bill is entirely on them.
Issued by:
Anna Maria Riezinger, Fiduciary
The United States of America
In care of: Box 520994
Big Lake, Alaska 99652
http://www.paulstramer.net/2024/07/international-public-notice-bear-in.html
Circles
Posts
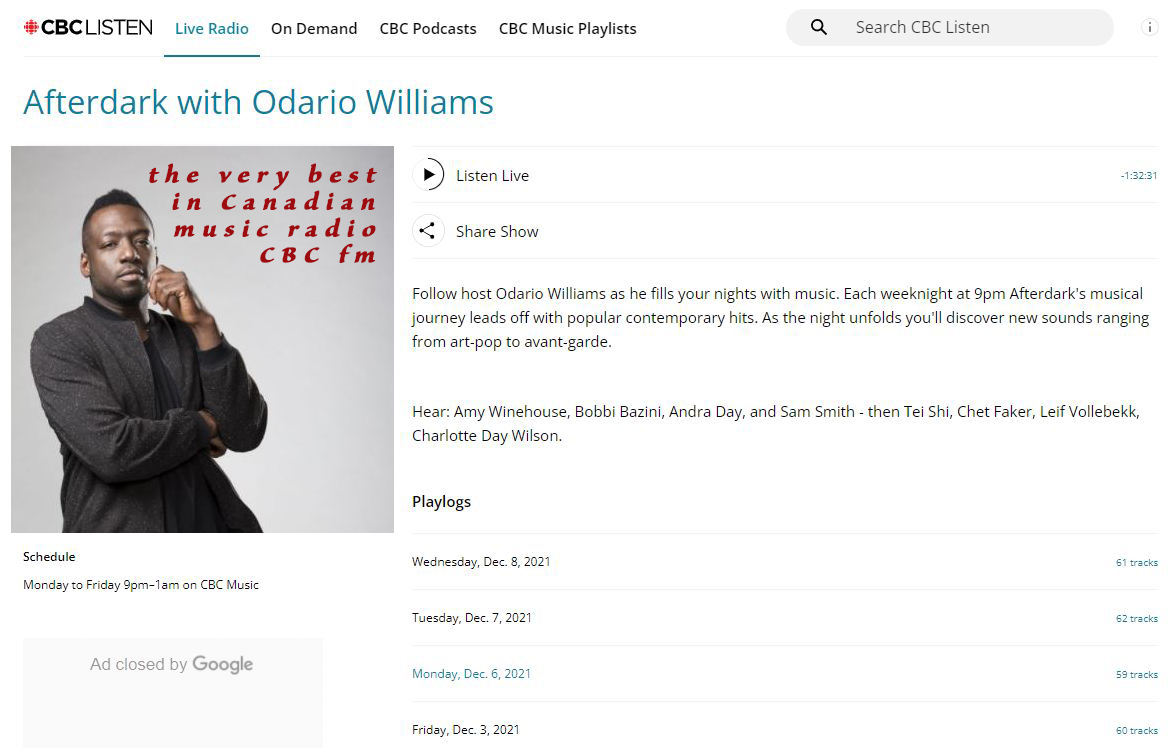
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Videos
Welcome to The Daily Wrap Up, a concise show dedicated to bringing you the most relevant independent news, as we see it, from the last 24 hours.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/2019-samoa-plandemic-test-run-outbreak-that-followed-dangerous-nih-eliquis-push
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get a TLAV "Question Everything" T-Shirt or Sticker at:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Afterhours_Live
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Parler: https://parler.com/TLAVagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
Bastyon: https://bastyon.com/tlavagabond
Flote: https://flote.app/LastAmericanVagabond
#TLAVPirateStreams #TheDailyWrapUp #TheLastAmericanVagabond
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Circles
Videos
Welcome to The Daily Wrap Up, a concise show dedicated to bringing you the most relevant independent news, as we see it, from the last 24 hours.
All Video Source Links Can Be Found Here At The Last American Vagabond: https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/2019-samoa-plandemic-test-run-outbreak-that-followed-dangerous-nih-eliquis-push
Want to send a check to support TLAV, or just words of encouragement?
Use our new P.O. box:
Ryan Cristian
1113 Murfreesboro Rd. Ste 106-146
Franklin, Tn 37064
Get a TLAV "Question Everything" T-Shirt or Sticker at:
https://truthclothing.io/collections/tlav
Like What You See? Help Us Stay People Funded:
https://tlavagabond.substack.com/
https://www.thelastamericanvagabond.com/donations/donation-form/
https://www.subscribestar.com/the-last-american-vagabond
https://cash.app/$TLAVagabond
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/tlavagabond
Bitcoin Donations: 3HybuDuvH4x5uJHemgc7EW4ms2nz3F8Gah
Ethereum Donations: 0x5e68B8984d9D8167dAf890588a7037Ae6Cc87d4b
Litecoin Donations: MX3T2kYvzfD4mNS4VNSyXFgY4abhUJC5ff
Bitcoin Cash Donations: qqsef23980qu5nlk2dj7s7ezwedl4fmy2gl2mxp9dp
Support The Last American Vagabond by Subscribing here:
http://www.feedblitz.com/f/?Sub=906867
The Last American Vagabond Links:
Sovern: https://sovren.media/u/tlavagabond/
Rumble: https://rumble.com/user/TheLastAmericanVagabond
Odysee: https://odysee.com/@TLAVagabond:5
Rokfin: https://www.rokfin.com/TLAVagabond
Minds: https://www.minds.com/TLAVagabond
Bitchute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/24yVcta8zEjY/
Telegram: https://t.me/TLAVagabond
VK: https://vk.com/id504366611
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Afterhours_Live
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/the_last_american_vagabond/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thelastamericanvagabond
Parler: https://parler.com/TLAVagabond
Getter: https://gettr.com/user/tlavagabond
TruthSocial: https://truthsocial.com/@TLAVagabond
Locals: https://thelastamericanvagabond.locals.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/Vagabond-Censored-103475109010293/
Memo: https://memo.cash/profile/1Np4Z2d25RSsQi99gKhf2cd5CAwN57jk13
MeWe: https://mewe.com/profile/5bcfb5d2a5f4e5420d7d5a2f
Bastyon: https://bastyon.com/tlavagabond
Flote: https://flote.app/LastAmericanVagabond
#TLAVPirateStreams #TheDailyWrapUp #TheLastAmericanVagabond
"Copyright Disclaimer Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for "fair use" for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research. Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing. Non-profit, educational or personal use tips the balance in favor of fair use.”
Posts
International Public Notice: The Bear in the China Shop
By Anna Von Reitz
The following brief case commentary from the United States Supreme Court (the Federal Republic Court in 1805) comes from a Law Memorandum written by the immortal John Trowbridge in which he is at pains to explain the difference between confederate states (States of America) operating the Federal Republic under The Constitution for the united States of America and the District States created by General Washington as administrative units of the Territorial District of Columbia Government and all of these "states" versus the Territories and Possessions of the United States known as the "Insular States":
"The Supreme Court explains the political distinction between, on the one hand, the members of
the Union, and on the other, the District of Columbia and the territories:
"On the part of the plaintiffs, it has been urged that Columbia is a distinct political society, and is therefore “a state” according to the definitions of writers on general law.
This is true. But as the act of Congress obviously uses the word “state” in reference to the term as used in the Constitution, it becomes necessary to inquire whether Columbia is a state in the sense of that instrument.
The result of that examination is a conviction that
the members of the American confederacy only are the states contemplated in the Constitution.
. . . These clauses show that the word “state” is used in the Constitution as designating a member of the union [of the original Confederation doing business as the States of America], and excludes from the term the signification attached to it by writers on the law of nations."
[Underline and boldface emphasis added.] Hepburn & Dundas v. Ellzey, 6 U.S. 445, 452, 2 Cranch 445, 2 L.Ed. 332 (1805).
"It has been attempted to distinguish a Territory from the district [sic] of Columbia; but the court is of opinion that this distinction cannot be maintained.
They may differ in many respects, but neither of them is a state, in the sense in which that term is used in the constitution."
[Emphasis added.] New Orleans v. Winter, 1 Wheat. (U. S.) 91, 4 L. Ed. 44 (1816).
These are definitive findings of the actual Federal Republic Supreme Court having the proper jurisdiction to decide these issues and what we herein discover is that:
The various kinds of "territories" either created administratively by the district of Columbia or arising as natural properties (Insular States) are not the "states" referenced in the Constitution.
The "states" in the Constitution being referenced in 1805 are the Confederate states, that is "states of state" that were members of the American Confederation formed in 1781 and known as "the American Confederacy" long before Jefferson Davis was born.
This all makes sense, as the American States of States were the members of the States of America -- that is, the Confederation -- awarded the Federal Constitution known as "The Constitution for the united States of America" in 1787.
Secondly, neither the district of Columbia nor the Territories attached to it are "states" of this kind.
As we put it in our second International Public Notice addressed to Derek Johnson, George Washington created District States, not state districts; the government of the district called "Columbia" is distinct and its "states" are distinct both from the Confederate states and the United States Territories, even though all three might meet the definition of "state" contemplated more generally under international law.
These two Supreme Court cases tell us that within the purview of the Constitution forming the Federal Republic the only "states" contemplated are the members of the original American Confederacy.
This distinction explains how we have (1) an American Federal Subcontractor, dba, States of America, and its states which are members of the American Confederacy, and (2) a district of Columbia Subcontractor and its territories (District States) which are not "states" within the meaning of the Federal Constitution, and (3) separate United States Territories and Possessions which are not "states" in this context, either.
Now you can better contemplate the complexity of the original Federal Government structure and discern how the use of the word "state" was contextually used to mean some states and not others.
For Constitutional purposes, the word "state" refers to the Confederate states belonging to the "States of America", the doing-business-as name of the original Confederation formed in 1781 which was awarded The Constitution for the united States of America in 1787. This is the Federal Government known as the Federal Republic.
In the original Federal Constitution (1787), the word "state" does not refer to the District States set up by George Washington to administer the district of Columbia and its territories (1789 Constitution), nor does it refer to the United States Territories and Possessions as "states" (1790 Constitution).
To summarize:
(1) We have the Union States that occupy the national soil jurisdiction of each nation-state.
(2) We have the Federation States that occupy the international land and sea jurisdiction belonging to each nation-state, and the members of the Federation, called States of the Union.
(3) We had the Confederate States (States-of-States) that were members of the original 1781 Confederation that occupied the global air jurisdiction belonging to each nation-state, and which were known jointly as "the American Confederacy".
(4) We had the above-mentioned Confederation doing business as the States of America and operating the Federal Republic under the 1787 Constitution for the united States of America until 1861 when the American Confederacy lost the necessary quorum to conduct business; at which point, the individual "Federal Republics" operated as another form of "states" also failed.
(5) We still have the District States arising under the Northwest Ordinance and territories of the district of Columbia, sometimes called "Federal enclaves", or Federal Management Units, Judicial Districts, Military Districts, etc.
(6) We still have the United States Territories and Possessions, sometimes called "the Insular States".
All of six of these governmental entities, three American and three Federal, have given rise to "states" and it behooves us to know this and to know that the general meaning of "states" accepted by the Law of Nations is not used in Federal Codes and documents; since early on, each document or Act of Congress defines the word "state" as a legal term for the purposes of that document, treaty, or code.
You can now see why this is necessary.
Our Union States and our States of the Union have never stood under any Constitution.
The American Federation of States that the "Federal Government" is named after, delegated the "enumerated powers" to the Federal Subcontractors.
The Federation could never stand under any Constitution as a result of this role, and neither could its member States.
The only form of American "State" to subject themselves and their Confederation to service under a Constitution were the original Confederate States of America (1781 to 1861) and these were all "States of States" -- separate organizations in the business of providing governmental services under contract.
None of these above referenced "states" known as the Union States or as the States of the Union nor as the original Confederate States were of any Territorial origin. They were (in the case of the Confederacy) or are (in the case of the Union States and Federation States) of uniquely American origin.
The District (that is, Territorial) States are a different story and arise on paper as a result of duties owed by the British Territorial Subcontractors under the Northwest Ordinance.
Likewise, the so-called Insular States, Puerto Rico, Guam, American Samoa, et alia, are known as territorial states and possessions of the United States.
All this tangled history, all these various kinds of "states" -- both those currently existing and those that are "missing" and awaiting reconstruction -- have to be separately known and acknowledged and defined, their powers and relationships accounted for, or it is literally impossible to know what you mean by "United States" or "States of America" or "United States of America".
The later incorporation of the British Territorial version of "the United States of America" to create "the United States of America -- Incorporated" added another layer of complexity, as we must additionally distinguish between incorporated and unincorporated "states".
Still later, the Municipal Government of the United States also incorporated Municipal Corporations named after our States, distinguished as STATES, which are foreign Municipal Corporations.
These additional incorporated "states" and "states of states" just muddy the water more and cause more confusion and these are business entities only, arising on paper; they are owned and operated by the Federal Subcontractors, not the American people.
Bottom line: we have been feloniously impersonated and so have our States of the Union.
We have been "assumed" to be responsible for the debts and outrages of these foreign corporations and their "states", without our knowledge or consent.
We have been "presumed to acquiesce" to their activities apportioning themselves new rights, new roles, and new empowerments, including but not limited to more than fifteen unilateral and unratified (by our States) Amendments to their service contracts, and endless drafts against our credit, and the unregulated enforcement of vast quantities of new Federal Code, representing impositions that were never granted to them via any contract.
Let it be known that these Subcontractors never consulted nor fully informed their employers of their actions and presumptions and never bothered to actually implement the remedies published as a means to legalize their theft of American property.
This leads to the inevitable conclusion that these foreign Employees working as Federal Subcontractors, used the plethora of confusions related to the kind and nature of "states", and the absence of the American Confederacy after the Civil War, to promote a mammoth and secretive fraud scheme against their actual Employers.
The absence of the American Confederacy in no way excuses their obligations owed to the American People and to the States of the Union and the Union States.
The absence of the American Confederacy doesn't grant them any additional contracts or special powers. It doesn't elevate or change the nature of their "states". It doesn't ratify all the unratified "Amendments" they have unilaterally made to their own service contracts. It doesn't allow them to declare war. It doesn't allow them to impersonate Americans as "Federal Citizens" via undisclosed and unconscionable registrations and enrollments and enlistments. It doesn't allow them to impersonate our Federation of States as a foreign incorporated entity.
The American Confederacy was never their Employer, and its duties were never vouchsafed to them.
Their gross failure to fully inform the Federation of States that delegated their "powers" to them, and their subsequent criminal activities resulting in gross harm to their employers speak for themselves.
These "Federal Corporations" have been operating as rogue "states" -- and they are not "states" of ours.
We have only by dint of our own hard work and investigation determined what these foreign entities have done "in our names" and falsely alleged against our country and our people. No disclosure was provided to us or to our States of the Union by these criminal miscreants, who are the responsibility of the Pope and His Imperial Majesty, "King" Charles, and the Lord Mayor of London.
There is no contract or agreement allowing our Federal Subcontractors to promote a Mercenary Conflict on our shores and the continuation of this illegal and immoral nonsense for 164 years in view of the fact that both these organizations are ultimately owned and operated by the Pope -- directly in the case of the Municipal Corporations, and indirectly through his Commonwealth Overseer in the case of the Territorial Corporations --- is purely criminal.
The Popes and the British Monarchs and the Governors and Mayors of Westminster have owed us good faith service throughout the duration of this self-interested crime spree, and they have fraudulently pretended to be our protectors, allies, and custodians throughout this criminal rampage of predation and impersonation, racketeering, human trafficking, and political usurpation.
The shame and the bill is entirely on them.
Issued by:
Anna Maria Riezinger, Fiduciary
The United States of America
In care of: Box 520994
Big Lake, Alaska 99652
http://www.paulstramer.net/2024/07/international-public-notice-bear-in.html
For a night time wind down and a relaxing mind set, check out CBC FM radio's AFTERDARK With Odario Williams. International music we think you will enjoy exploring is sprinkled throughout. https://www.cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark
#afterdark #OdarioWilliams #CBCfm #radio #fm #Canada #NorthAmerica #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Australia has a day time radio broadcasting to the Pacific and the world, #ABCRadioAustralia is ready to lift your spirits with the happy sounds. Just click here: https://abc.net.au/pacific/live #Australia #radio #music #Pacific #NorthAmerica #EastAsia #CentralAmerica #SouthAmerica #day #Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
Very best late night music radio station, we recommend, AFTERDARK With Odario Williams on CBC radio FM Canada. Fine selection of international sounds sprinkled throughout: https://cbc.ca/listen/live-radio/1-1051-afterdark #AFTERDARK #CBCfm #radio #music #Canada #world #Europe #Asia #Africa #SouthAmerica
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe
For the very best in Japanese news, social news and entertainment MIDNIGHT AT THE COFFEE SHOP recommends: TJS Radio. Just click here: https://radio.net/s/tjsradio #Japan #TJSradio #radio #Japan #NorthAmerica #Japanese #Canada #news #entertainmentNews #social
#Afghanistan #Albania #Algeria #Andorra #Angola #AntiguaandBarbuda #Argentina #Armenia #Australia #Austria #Azerbaijan #Bahamas #Bahrain #Bangladesh #Barbados #Belarus #Belgium #Belize #Benin #Bhutan #Bolivia #BosniaandHerzegovina #Botswana #Brazil #Brunei #Bulgaria #BurkinaFaso #Burundi #CaboVerde #Cambodia #Cameroon #Canada #CentralAfricanRepublic #Chad #Chile #China #Colombia #Comoros #CongoDemocraticRepublicofthe #CongoRepublicofthe #CostaRica #CotedIvoire #Croatia #Cuba #Cyprus #Czechia #Denmark #Djibouti #Dominica #DominicanRepublic #Ecuador #Egypt #ElSalvador #EquatorialGuinea #Eritrea #Estonia #Eswatini #Ethiopia #Fiji #Finland #France #Gabon #Gambia #Georgia #Germany #Ghana #Greece #Grenada #Guatemala #Guinea #GuineaBissau #Guyana #Haiti #Honduras #Hungary #Iceland #India #Indonesia #Iran #Iraq #Ireland #Israel #Italy #Jamaica #Japan #Jordan #Kazakhstan #Kenya #Kiribati #Kosovo #Kuwait #Kyrgyzstan #Laos #Latvia #Lebanon #Lesotho #Liberia #Libya #Liechtenstein #Lithuania #Luxembourg #Madagascar #Malawi #Malaysia #Maldive #Mali #Malta #MarshallIslands #Mauritania #Mauritius #Mexico #Micronesia #Moldova #Monaco #Mongolia #Montenegro #Morocco #Mozambique #Myanmar #Namibia #Nauru #Nepal #Netherlands #NewZealand #Nicaragua #Niger #Nigeria #NorthKorea #NorthMacedonia #Norway #Oman #Pakistan #Palau #Palestine #Panama #PapuaNewGuinea #Paraguay #Peru #Philippines #Poland #Portugal #Qatar #Romania #Russia #Rwanda #SaintKittsandNevis #SaintLucia #SaintVincentandtheGrenadines #Samoa #SanMarino #SaoTomeandPrincipe #SaudiArabia #Senegal #Serbia #Seychelles #SierraLeone #Singapore #Slovakia #Slovenia #SolomonIslands #Somalia #SouthAfrica #SouthKorea #SouthSudan #Spain #SriLanka #Sudan #Suriname #Sweden #Switzerland #Syria #Taiwan #Tajikistan #Tanzania #Thailand #TimorLeste #Togo #Tonga #TrinidadandTobago #Tunisia #Turkey #Turkmenistan #Tuvalu #Uganda #Ukraine #UnitedArabEmirates #UnitedKingdom #USA #Uruguay #Uzbekistan #Vanuatu #VaticanCity #Venezuela #Vietnam #Yemen #Zambia #Zimbabwe