#MainstreamMedia pushing risky #weightloss #vaccines on the masses #bigpharma
https://www.naturalnews.com/2024-07-25-mainstream-media-big-pharma-promote-weight-loss-injections.html
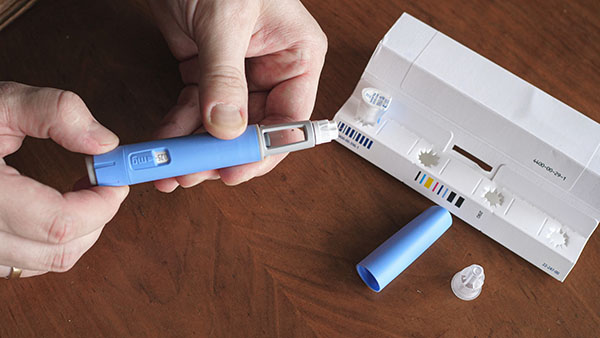
The mainstream media has long been used to advertise for and support the pharmaceutical industry, and anyone who has ever doubted this is the case was proven wrong by the way the media handled COVID-19 vaccines. Now, the “solution” they’re pushing on the masses is the weight loss drug Ozempic and others of its ilk, […]
www.naturalnews.com