GRAND DADDY PURPLE VAPE CART – DELTA 8 THC – FRESH – 900MG
BUY DELTA 8 CARTS ONLINE IN WANGARATTA
Buy Delta 8 Carts Online In Wangaratta. Have you used your delta 8 vape cart recently? Does each puff taste sweet, delicious, and full of hemp extract and natural terpenes? With delta 8 thc vape carts you should get a taste of smooth vape juice that stimulates your senses and calms your body at the same time. After all, you deserve something Fresh! Well, you get just that and more with Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts now in Grand Daddy Purple. It’s 900mg of hemp extract and natural terpenes fresh from the field with a pure buzz you soon won’t forget.
What makes Fresh brand delta 8 vape carts different? First, we grow all of our hemp by hand outdoors. Each plant enjoys peak conditions under the sun in the clean — and Fresh! — American air. Next, we use only the purest, most natural delta 8 thc, filled with sweet-smelling terpenes that give every strain a unique feeling. When you taste it, you’re feeling the buzz for the very first time. Grape Ape Vape Cart – Delta 8 THC – Fresh – 900MG
And this time, Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts will have you feeling the buzz in everyone’s favorite flavor known as Grand Daddy Purple. Hard to pin down, this fast moving indica has many names, including Grand Daddy Purps and GDP, but it always comes to play. Buy Delta 8 Carts Online In Wangaratta. You’ll feel a mix of cerebral euphoria, body relaxation, and a nice, dreamy buzz. Grand Daddy Purple Vape Cart – HHC – Fresh – 900MG
Try Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts in Grand Daddy Purple today and see what 900mg of sweet, clean, and pure hemp-derived delta 8 can do for you. We use only the freshest processes to cultivate our hemp and extract our cannabinoids, and all of our compounds are third-party tested for your safety. When you vape Fresh, you’re guaranteed the best, safest, and Freshest D8 on the market today! Delta 8 gummies for Sale In Australia Grape Ape Vape Cart – Delta 8 THC – Fresh – 900MG
https://we4high.com/product-category/delta-8-disposable-vape-australia
People
Circles
Posts
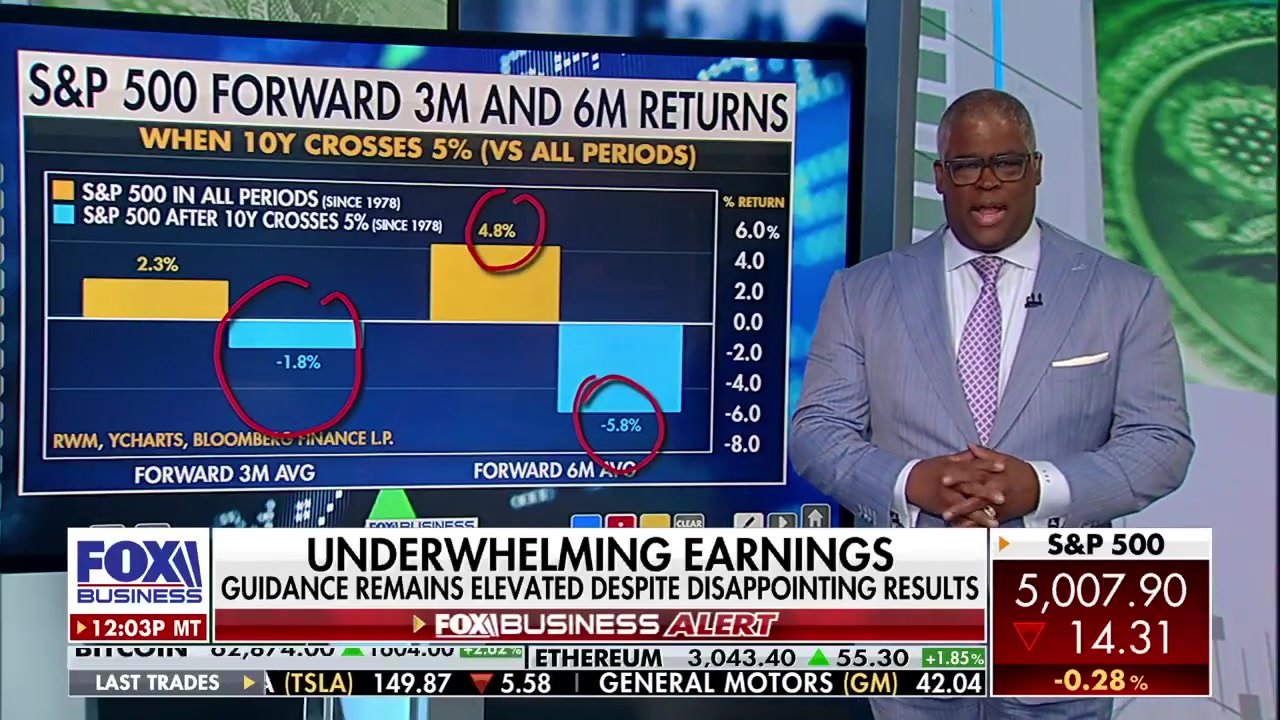
Wall Street legend shows which parts of the market are 'overvalued'
https://www.brighteon.com/0effa88d-3268-438c-a373-f91223bbd948
123ba3 com đã được công nhận là một trong những nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu tại thị trường Việt Nam. Với sự đa dạng trong các trò chơi cá cược trực tuyến như tài xỉu, xóc đĩa, bắn cá và casino trực tuyến, họ đã thu hút được sự tin tưởng và sự quan tâm từ người chơi khắp nơi.
Tên doanh nghiệp: 123b
Website: https://123ba3.com/
Mail: 123ba3com@gmail.com
Hotline: 0972777999
Địa chỉ: 24 Hoàng Sâm, Nghĩa Đô, Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội
#23b#23ba3#123ba3com
https://twitter.com/123b448629
https://www.pinterest.com/123ba3com/
https://www.youtube.com/@123ba3com
https://www.reddit.com/user/123ba3com/
https://www.twitch.tv/123ba3com/about
https://sovren.media/u/123ba3com/
https://goodjobdongguan.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4136816
https://www.vid419.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3381199
http://winnipeg.pinklink.ca/author/123ba3com/
http://classicalmusicmp3freedownload.com/ja/index.php?title=%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8%E8%80%85:123ba3com
https://webarticleservices.com/members/123ba3com/
https://6giay.vn/members/123ba3com.68554/
https://jszst.com.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3281883
https://m.jingdexian.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2714262
https://chillspot1.com/user/123ba3com
https://www.xibeiwujin.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2222671
https://writexo.com/6uua9p20
https://www.deepzone.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=3368411
https://phenomenalarticles.com/members/123ba3com/
https://www.teafish.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=3397362
http://www.disonde.com/jishu/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=1535430
https://www.yanyiku.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3536998
https://www.anibookmark.com/user/123ba3com.html
http://bbs.01bim.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360094
http://emseyi.com/user/123ba3com
http://www.so0912.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2172480
https://matkafasi.com/user/123ba3com
https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:123ba3com
https://gitlab.vuhdo.io/123ba3com
https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/2024/03/viva88.html'>https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/2024/03/viva88.html
https://offroadjunk.com/questions/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=123ba3com
https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/
https://hukukevi.net/user/123ba3com
https://hangoutshelp.net/user/viva888wiki/wall
https://web.ggather.com/123ba3com
https://www.asklent.com/user/123ba3com
https://kaeuchi.jp/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://www.hahalolo.com/@123ba3com
http://www.freeok.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=5332513
https://www.hydroworxirrigation.com/profile/liquetgrimstead229/profile
https://kerbalx.com/123ba3com
https://eternagame.org/players/368751
https://code.datasciencedojo.com/123ba3com
https://docvino.com/members/123ba3com/profile/
https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/123b-11
https://www.darkml.net/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=7946360&do=profile&from=space
https://www.claimajob.com/profiles/4556594-123b-com
https://demo.hedgedoc.org/Gen6rXT1QdG66U2EmSp5rw?view
https://meetup.furryfederation.com/events/e557390c-d61f-427b-afcc-7d2f074c1396
https://www.bondhuplus.com/123ba3com
http://planforexams.com/q2a/user/123ba3com
https://macro.market/company/123b-6
https://bbs.weipubao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3784707
https://1ctv.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=2948101
https://community.fyers.in/member/fbaTN0klDm
https://infodin.com.br/index.php/User:123ba3com
https://my.djtechtools.com/users/1402751
https://youdontneedwp.com/123ba3com/my-new-post-4346aec5-0a65-4e9a-948e-6c0b433951c5
https://pytania.radnik.pl/uzytkownik/123ba3com/wall
https://biiut.com/123ba3com
https://personaljournal.ca/123ba3com/123b
https://justpaste.me/xoLG1
https://fontstruct.com/fontstructors/2427509/123ba3com
https://www.outdoorproject.com/users/123ba3-com
https://schoolido.lu/user/123ba3com/
https://eorzea.photos/i/web/profile/686930910082772661
https://qna.habr.com/user/123ba3com
https://wiki.gta-zona.ru/index.php/%D0%9E%D0%B1%D1%81%D1%83%D0%B6%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5_%D1%83%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B0:123b
https://g0v.hackmd.io/b7WvYC-yQECYLUvQOwcJyA?view
https://hackmd.okfn.de/vXk2fKLSQqSntDVpXmYFBQ?view
https://glitch.com/@123ba3com
https://research.openhumans.org/member/123ba3com/
https://wiki.author-alarm.ru/index.php/%D0%A3%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA:123ba3com
https://wibki.com/GrimsteadLiquet
https://olderworkers.com.au/author/liquetgrimstead229gmail-com/
https://www.laundrynation.com/community/profile/123ba3com/
https://linguacop.eu/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://onlyfans.com/u412133690
https://www.elephantjournal.com/profile/liquetgrimstead229/
https://forum.liquidbounce.net/user/123ba3com
https://turkish.ava360.com/user/123ba3com/
https://prosinrefgi.wixsite.com/pmbpf/profile/liquetgrimstead229/profile
http://linktaigo88.crowdfundhq.com/users/123b-124
https://divisionmidway.org/jobs/author/123ba3com/
https://historydb.date/wiki/User:123ba3com
https://www.strata.com/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://drivehud.com/forums/users/liquetgrimstead229/
https://sites.google.com/view/123ba3com/home
https://www.fitday.com/fitness/forums/members/123ba3com.html
https://socialtrain.stage.lithium.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/57227
https://artistecard.com/123ba3com
https://123ba3com.hashnode.dev/123b
https://postheaven.net/rwu45ha9in
https://pastelink.net/vwwnedqw
https://www.rctech.net/forum/members/123ba3com-365973.html
https://www.rcuniverse.com/forum/members/123ba3com.html
https://kktix.com/user/5927227
https://www.beamng.com/members/123ba3com.599965/
https://timeoftheworld.date/wiki/User:123ba3com
http://jobboard.piasd.org/author/123ba3com/
https://123b-10.gitbook.io/123b/
https://talk.plesk.com/members/123ba3com.334649/#about
https://www.behance.net/123ba3com
https://sketchfab.com/123ba3com
https://flipboard.com/@123b2rsf/123b-3phih3aey
https://hackerone.com/123ba3com?type=user
https://www.magcloud.com/user/123ba3com
https://filmow.com/usuario/123ba3com
Videos
On this episode of The Cost of Everything, dive into the current realities of renting. Host Christy Ai investigates the financial burdens faced by renters, who often find themselves funding others’ investments due to the challenges of high interest rates and a fiercely competitive housing market. Joining the discussion is real estate economist Ken Johnson, who sheds light on the factors influencing renting trends among specific cities and generations, and the obstacles hindering the pursuit of the American dream of homeownership.
The unprecedented and unrelenting rise in stocks has an ominous feeling to it. Like the legendary crack-up booms of bubble past. Also, we discuss the CBO’s projections of the next ten years of US deficits, that only grow and grow hitting an eye-watering $2.7 trillion/yr in 2034. Obviously something breaks along that path. Are you ready?
Want a free no obligation review with Paul and his team? Click here www.PeakFinancialInvesting.com
Join the conversation here:
http://tinyurl.com/FinanceU2
For more information on our amazing new webinar series - Prospering With Integrity with Bret Weinstein, Ed Dowd and Peter St Onge, click here:
http://peak.fan/integrity
First and second episodes available now!. Use PWI25 today for 25% off the series, or join under an annual subscription to PeakProsperity.com with Peak30 and get access to the webinar series FREE!
? NOTE: Annual members to PeakProsperity.com get all episodes of Prospering with Integrity (and much more!) as a perk of the subscription. Watch more of our videos here to find hidden codes to use on our membership! ?️♂️?
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee?
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter:
@Chris_martenson
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
Gettr: @PeakProsperity (NEW!)
Truth Social: @PeakProsperity (NEW!)
Instagram: peak.prosperity
Several indicators are screaming “recession!” But the “”markets”” are happily rising higher all over the globe on an obvious wall of central bank liquidity. Can ‘they’ print us out of the nose-dive? What if they don’t? What should investors be considering? Tune in to find out.
Want a free no obligation review with Paul and his team? Click here www.PeakFinancialInvesting.com
Join the conversation here: https://peakprosperity.com/is-a-recession-on-the-way-finance-university-with-paul-kiker/
For more information on our amazing new webinar series - Prospering With Integrity with Bret Weinstein, Ed Dowd and Peter St Onge, click here:
http://peak.fan/integrity
First and second episodes available now!. Use PWI25 today for 25% off the series, or join under an annual subscription to PeakProsperity.com with Peak30 and get access to the webinar series FREE!
? NOTE: Annual members to PeakProsperity.com get all episodes of Prospering with Integrity (and much more!) as a perk of the subscription. Watch more of our videos here to find hidden codes to use on our membership! ?️♂️?
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee? https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter: @Chris_martenson
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
Circles
Videos
On this episode of The Cost of Everything, dive into the current realities of renting. Host Christy Ai investigates the financial burdens faced by renters, who often find themselves funding others’ investments due to the challenges of high interest rates and a fiercely competitive housing market. Joining the discussion is real estate economist Ken Johnson, who sheds light on the factors influencing renting trends among specific cities and generations, and the obstacles hindering the pursuit of the American dream of homeownership.
The unprecedented and unrelenting rise in stocks has an ominous feeling to it. Like the legendary crack-up booms of bubble past. Also, we discuss the CBO’s projections of the next ten years of US deficits, that only grow and grow hitting an eye-watering $2.7 trillion/yr in 2034. Obviously something breaks along that path. Are you ready?
Want a free no obligation review with Paul and his team? Click here www.PeakFinancialInvesting.com
Join the conversation here:
http://tinyurl.com/FinanceU2
For more information on our amazing new webinar series - Prospering With Integrity with Bret Weinstein, Ed Dowd and Peter St Onge, click here:
http://peak.fan/integrity
First and second episodes available now!. Use PWI25 today for 25% off the series, or join under an annual subscription to PeakProsperity.com with Peak30 and get access to the webinar series FREE!
? NOTE: Annual members to PeakProsperity.com get all episodes of Prospering with Integrity (and much more!) as a perk of the subscription. Watch more of our videos here to find hidden codes to use on our membership! ?️♂️?
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee?
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter:
@Chris_martenson
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
Gettr: @PeakProsperity (NEW!)
Truth Social: @PeakProsperity (NEW!)
Instagram: peak.prosperity
Several indicators are screaming “recession!” But the “”markets”” are happily rising higher all over the globe on an obvious wall of central bank liquidity. Can ‘they’ print us out of the nose-dive? What if they don’t? What should investors be considering? Tune in to find out.
Want a free no obligation review with Paul and his team? Click here www.PeakFinancialInvesting.com
Join the conversation here: https://peakprosperity.com/is-a-recession-on-the-way-finance-university-with-paul-kiker/
For more information on our amazing new webinar series - Prospering With Integrity with Bret Weinstein, Ed Dowd and Peter St Onge, click here:
http://peak.fan/integrity
First and second episodes available now!. Use PWI25 today for 25% off the series, or join under an annual subscription to PeakProsperity.com with Peak30 and get access to the webinar series FREE!
? NOTE: Annual members to PeakProsperity.com get all episodes of Prospering with Integrity (and much more!) as a perk of the subscription. Watch more of our videos here to find hidden codes to use on our membership! ?️♂️?
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee? https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter: @Chris_martenson
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
In our talk today, Paul and I discuss the fascinating yet alarming surge in market valuations, a trend unseen since the seven weeks of 1929. We delve into John Hussman’s recent market commentary and how these high valuations contrast with the longest anticipated, yet unrealized, recession.
Want a free no obligation review with Paul and his team? Click here www.PeakFinancialInvesting.com
Join the conversation here: https://peakprosperity.com/unlocking-insights-and-unveiling-economic-realities/
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee? https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter: @Chris_martenson
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
Last week the Fed threw us a curveball. Their dovish pivot wasn’t just a minor adjustment; it was a seismic shift that sent shockwaves through the markets. The Dow soared to an unprecedented high, and even the Nasdaq, not one to be left behind, either matched or surpassed its peak this morning.
Order THE CRASH COURSE here:
https://www.barnesandnoble.com/w/the-crash-course-chris-martenson/1142015889?ean=9781394168866
Wanna buy me a coffee? https://www.buymeacoffee.com/PeakProsperity
Join the #1 resilience community today!
https://peakprosperity.com/membership/
FINANCIAL DISCLAIMER. PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC, AND PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE NOT ENGAGED IN RENDERING LEGAL, TAX, OR FINANCIAL ADVICE OR SERVICES VIA THIS WEBSITE. NEITHER PEAK PROSPERITY, LLC NOT PEAK FINANCIAL INVESTING ARE FINANCIAL PLANNERS, BROKERS, OR TAX ADVISORS. Their websites are intended only to assist you in your financial education. Your personal financial situation is unique, and any information and advice obtained through this website may not be appropriate for your situation. Accordingly, before making any final decisions or implementing any financial strategy, you should consider obtaining additional information and advice from your accountant or other financial advisers who are fully aware of your individual circumstances. All information in this video is as accurate as we believe them to be based on current market conditions at the time of recording.
ALSO FOLLOW US HERE:
Twitter: @Chris_martenson
https://rumble.com/c/PeakProsperity
https://odysee.com/@Chris_Martenson:2
Posts
GRAND DADDY PURPLE VAPE CART – DELTA 8 THC – FRESH – 900MG
BUY DELTA 8 CARTS ONLINE IN WANGARATTA
Buy Delta 8 Carts Online In Wangaratta. Have you used your delta 8 vape cart recently? Does each puff taste sweet, delicious, and full of hemp extract and natural terpenes? With delta 8 thc vape carts you should get a taste of smooth vape juice that stimulates your senses and calms your body at the same time. After all, you deserve something Fresh! Well, you get just that and more with Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts now in Grand Daddy Purple. It’s 900mg of hemp extract and natural terpenes fresh from the field with a pure buzz you soon won’t forget.
What makes Fresh brand delta 8 vape carts different? First, we grow all of our hemp by hand outdoors. Each plant enjoys peak conditions under the sun in the clean — and Fresh! — American air. Next, we use only the purest, most natural delta 8 thc, filled with sweet-smelling terpenes that give every strain a unique feeling. When you taste it, you’re feeling the buzz for the very first time. Grape Ape Vape Cart – Delta 8 THC – Fresh – 900MG
And this time, Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts will have you feeling the buzz in everyone’s favorite flavor known as Grand Daddy Purple. Hard to pin down, this fast moving indica has many names, including Grand Daddy Purps and GDP, but it always comes to play. Buy Delta 8 Carts Online In Wangaratta. You’ll feel a mix of cerebral euphoria, body relaxation, and a nice, dreamy buzz. Grand Daddy Purple Vape Cart – HHC – Fresh – 900MG
Try Fresh Delta 8 THC Disposable vape carts in Grand Daddy Purple today and see what 900mg of sweet, clean, and pure hemp-derived delta 8 can do for you. We use only the freshest processes to cultivate our hemp and extract our cannabinoids, and all of our compounds are third-party tested for your safety. When you vape Fresh, you’re guaranteed the best, safest, and Freshest D8 on the market today! Delta 8 gummies for Sale In Australia Grape Ape Vape Cart – Delta 8 THC – Fresh – 900MG
https://we4high.com/product-category/delta-8-disposable-vape-australia
Wall Street legend shows which parts of the market are 'overvalued'
https://www.brighteon.com/0effa88d-3268-438c-a373-f91223bbd948
123ba3 com đã được công nhận là một trong những nhà cái uy tín hàng đầu tại thị trường Việt Nam. Với sự đa dạng trong các trò chơi cá cược trực tuyến như tài xỉu, xóc đĩa, bắn cá và casino trực tuyến, họ đã thu hút được sự tin tưởng và sự quan tâm từ người chơi khắp nơi.
Tên doanh nghiệp: 123b
Website: https://123ba3.com/
Mail: 123ba3com@gmail.com
Hotline: 0972777999
Địa chỉ: 24 Hoàng Sâm, Nghĩa Đô, Cầu Giấy, Hà Nội
#23b#23ba3#123ba3com
https://twitter.com/123b448629
https://www.pinterest.com/123ba3com/
https://www.youtube.com/@123ba3com
https://www.reddit.com/user/123ba3com/
https://www.twitch.tv/123ba3com/about
https://sovren.media/u/123ba3com/
https://goodjobdongguan.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4136816
https://www.vid419.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3381199
http://winnipeg.pinklink.ca/author/123ba3com/
http://classicalmusicmp3freedownload.com/ja/index.php?title=%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8%E8%80%85:123ba3com
https://webarticleservices.com/members/123ba3com/
https://6giay.vn/members/123ba3com.68554/
https://jszst.com.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3281883
https://m.jingdexian.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2714262
https://chillspot1.com/user/123ba3com
https://www.xibeiwujin.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2222671
https://writexo.com/6uua9p20
https://www.deepzone.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=3368411
https://phenomenalarticles.com/members/123ba3com/
https://www.teafish.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=3397362
http://www.disonde.com/jishu/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=1535430
https://www.yanyiku.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3536998
https://www.anibookmark.com/user/123ba3com.html
http://bbs.01bim.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360094
http://emseyi.com/user/123ba3com
http://www.so0912.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2172480
https://matkafasi.com/user/123ba3com
https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:123ba3com
https://gitlab.vuhdo.io/123ba3com
https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/2024/03/viva88.html'>https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/2024/03/viva88.html
https://offroadjunk.com/questions/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=123ba3com
https://123ba3com.blogspot.com/
https://hukukevi.net/user/123ba3com
https://hangoutshelp.net/user/viva888wiki/wall
https://web.ggather.com/123ba3com
https://www.asklent.com/user/123ba3com
https://kaeuchi.jp/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://www.hahalolo.com/@123ba3com
http://www.freeok.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=5332513
https://www.hydroworxirrigation.com/profile/liquetgrimstead229/profile
https://kerbalx.com/123ba3com
https://eternagame.org/players/368751
https://code.datasciencedojo.com/123ba3com
https://docvino.com/members/123ba3com/profile/
https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/123b-11
https://www.darkml.net/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=7946360&do=profile&from=space
https://www.claimajob.com/profiles/4556594-123b-com
https://demo.hedgedoc.org/Gen6rXT1QdG66U2EmSp5rw?view
https://meetup.furryfederation.com/events/e557390c-d61f-427b-afcc-7d2f074c1396
https://www.bondhuplus.com/123ba3com
http://planforexams.com/q2a/user/123ba3com
https://macro.market/company/123b-6
https://bbs.weipubao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3784707
https://1ctv.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=2948101
https://community.fyers.in/member/fbaTN0klDm
https://infodin.com.br/index.php/User:123ba3com
https://my.djtechtools.com/users/1402751
https://youdontneedwp.com/123ba3com/my-new-post-4346aec5-0a65-4e9a-948e-6c0b433951c5
https://pytania.radnik.pl/uzytkownik/123ba3com/wall
https://biiut.com/123ba3com
https://personaljournal.ca/123ba3com/123b
https://justpaste.me/xoLG1
https://fontstruct.com/fontstructors/2427509/123ba3com
https://www.outdoorproject.com/users/123ba3-com
https://schoolido.lu/user/123ba3com/
https://eorzea.photos/i/web/profile/686930910082772661
https://qna.habr.com/user/123ba3com
https://wiki.gta-zona.ru/index.php/%D0%9E%D0%B1%D1%81%D1%83%D0%B6%D0%B4%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5_%D1%83%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%B0:123b
https://g0v.hackmd.io/b7WvYC-yQECYLUvQOwcJyA?view
https://hackmd.okfn.de/vXk2fKLSQqSntDVpXmYFBQ?view
https://glitch.com/@123ba3com
https://research.openhumans.org/member/123ba3com/
https://wiki.author-alarm.ru/index.php/%D0%A3%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA:123ba3com
https://wibki.com/GrimsteadLiquet
https://olderworkers.com.au/author/liquetgrimstead229gmail-com/
https://www.laundrynation.com/community/profile/123ba3com/
https://linguacop.eu/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://onlyfans.com/u412133690
https://www.elephantjournal.com/profile/liquetgrimstead229/
https://forum.liquidbounce.net/user/123ba3com
https://turkish.ava360.com/user/123ba3com/
https://prosinrefgi.wixsite.com/pmbpf/profile/liquetgrimstead229/profile
http://linktaigo88.crowdfundhq.com/users/123b-124
https://divisionmidway.org/jobs/author/123ba3com/
https://historydb.date/wiki/User:123ba3com
https://www.strata.com/forums/users/123ba3com/
https://drivehud.com/forums/users/liquetgrimstead229/
https://sites.google.com/view/123ba3com/home
https://www.fitday.com/fitness/forums/members/123ba3com.html
https://socialtrain.stage.lithium.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/57227
https://artistecard.com/123ba3com
https://123ba3com.hashnode.dev/123b
https://postheaven.net/rwu45ha9in
https://pastelink.net/vwwnedqw
https://www.rctech.net/forum/members/123ba3com-365973.html
https://www.rcuniverse.com/forum/members/123ba3com.html
https://kktix.com/user/5927227
https://www.beamng.com/members/123ba3com.599965/
https://timeoftheworld.date/wiki/User:123ba3com
http://jobboard.piasd.org/author/123ba3com/
https://123b-10.gitbook.io/123b/
https://talk.plesk.com/members/123ba3com.334649/#about
https://www.behance.net/123ba3com
https://sketchfab.com/123ba3com
https://flipboard.com/@123b2rsf/123b-3phih3aey
https://hackerone.com/123ba3com?type=user
https://www.magcloud.com/user/123ba3com
https://filmow.com/usuario/123ba3com
789betrun info là điểm đến hàng đầu cho cá cược trực tuyến tại Châu Á, không chỉ mang đến những trò chơi hấp dẫn mà còn chia sẻ những kinh nghiệm cá cược online tuyệt vời, kèm theo một kho sản phẩm đa dạng và hấp dẫn.
Tên doanh nghiệp: 789bet
Điện thoại: 098256872
Gmail: 789betruninfo@gmail.com
Địa Chỉ: 59 P. Trần Huy Liệu, Giảng Võ, Ba Đình, Hà Nội, Việt Nam
Website: https://789betrun.info/
#789bet#789betrun#789betruninfo
https://twitter.com/DerenzisTr48610
https://vimeo.com/789betruninfo
https://www.pinterest.com/789betruninfo/
https://www.youtube.com/@789betruninfo
https://www.twitch.tv/789betruninfo/about
https://www.reddit.com/user/789betruninfo/
https://www.tumblr.com/789betruninfo
https://500px.com/p/789betruninfo?view=photos
https://glose.com/u/789betruninfo
https://digitaltibetan.win/wiki/User:789betruninfo
https://willysforsale.com/author/789betruninfo/
https://comicsdb.cz/profil/39061/789betruninfo
https://rotorbuilds.com/profile/37817
https://www.chaloke.com/forums/users/789betruninfo/
https://ekonty.com/-789betruninfo
https://connect.gt/user/789betruninfo
https://fkwiki.win/wiki/User:789betruninfo
https://theflatearth.win/wiki/User:789betruninfo
https://golbis.com/user/789betruninfo/
https://www.foroatletismo.com/foro/members/789betruninfo.html
https://sovren.media/u/789betruninfo/
https://goodjobdongguan.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4134144
https://www.vid419.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3381177
http://winnipeg.pinklink.ca/author/789betruninfo/
http://classicalmusicmp3freedownload.com/ja/index.php?title=%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8%E8%80%85:789betruninfo
https://scrapbox.io/789betruninfo/789bet
http://freestyler.ws/user/451749/789betruninfo
https://mecabricks.com/en/user/789betruninfo
https://webarticleservices.com/members/789betruninfo/
https://6giay.vn/members/789betruninfo.68485/
https://jszst.com.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3280404
https://m.jingdexian.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2712413
https://vietfones.vn/forum/members/789betruninfo.244249/
https://chillspot1.com/user/789betruninfo
https://www.xibeiwujin.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2222645&do=profile&from=space
https://writexo.com/share/ipgt2o16
https://www.mtg-forum.de/user/75875-789betruninfo/
https://www.deepzone.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=3366824
https://doselect.com/@derenzistrease769@gmail.com
https://phenomenalarticles.com/members/789betruninfo/
https://www.teafish.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=3395796
https://electrodb.ro/forums/users/789betruninfo/
http://www.disonde.com/jishu/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=1534271
https://www.yanyiku.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3535504
https://www.anibookmark.com/user/789betruninfo.html
http://bbs.01bim.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360067
http://emseyi.com/user/789betruninfo
http://www.so0912.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=2172104
https://matkafasi.com/user/789betruninfo
https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:789betruninfo'>https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:789betruninfo
https://gitlab.vuhdo.io/789betruninfo
https://789betruninfo.blogspot.com/2024/04/789bet.html'>https://789betruninfo.blogspot.com/2024/04/789bet.html
https://offroadjunk.com/questions/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=789betruninfo
https://789betruninfo.blogspot.com/
https://hukukevi.net/user/789betruninfo
https://hangoutshelp.net/user/789betruninfo
https://web.ggather.com/789betruninfo
https://www.asklent.com/user/789betruninfo
https://kaeuchi.jp/forums/users/789betruninfo/
https://www.hahalolo.com/@6621fbff0694371ea490983a
http://www.freeok.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=5330817
https://www.openrec.tv/user/789betruninfo/about
https://cuchichi.es/author/789betruninfo/
https://www.hydroworxirrigation.com/profile/derenzistrease769/profile
https://kerbalx.com/789betruninfo
https://eternagame.org/players/368657
https://code.datasciencedojo.com/derenzistrease769
https://docvino.com/members/789betruninfo/profile/
https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/789bet-27
https://www.claimajob.com/profiles/4555067-789betrun-info
https://meetup.furryfederation.com/events/b6ffbe3e-d3fc-4980-a184-d27e8b991c43
https://www.bondhuplus.com/789betruninfo
http://planforexams.com/q2a/user/789betruninfo
https://macro.market/company/789bet-23
https://bbs.weipubao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=3782545
https://myanimeshelf.com/profile/789betruninfo
http://1ctv.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=2948075
https://789betruninfo.notepin.co/
https://defolio.com/789bet
https://community.fyers.in/member/vaHJIRRlUa
https://infodin.com.br/index.php/User:789betruninfo
https://my.djtechtools.com/users/1402700
https://youdontneedwp.com/789betruninfo/789bet-10f75799-1f95-44f7-bc94-2be30495d511
https://pytania.radnik.pl/uzytkownik/789betruninfo
https://bit.ly/442R56B
https://biiut.com/789betruninfo
https://personaljournal.ca/789betruninfo/789bet
https://www.swanmei.com/space-uid-3616249.html
https://fontstruct.com/fontstructors/2427357/789betruninfo
https://www.outdoorproject.com/users/789betrun-info
https://eorzea.photos/789betruninfo
https://pellicule.bim.land/789betruninfo
https://linkmix.co/22688741
https://en.wikialpha.org/wiki/User:789betruninfo
https://qna.habr.com/user/789betruninfo
http://tf88ac.crowdfundhq.com/users/789bet
https://b.hatena.ne.jp/betruninfo789/
https://wiki.gta-zona.ru/index.php/%D0%A3%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA:789betruninfo
https://glitch.com/@789betruninfo
https://boersen.oeh-salzburg.at/author/789betruninfo/
https://emplois.fhpmco.fr/author/789betruninfo/
https://research.openhumans.org/member/789betruninfo/
https://wiki.author-alarm.ru/index.php/%D0%A3%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%BA:789betruninfo
https://m.wibki.com/789betruninfo
https://www.freelancejob.ru/users/789betruninfo/info.php
https://www.speedrun.com/users/789betruninfo
https://www.renderosity.com/users/id:1483622
https://dsred.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3500531
https://graphis.com/portfolios/789-betrun-info
https://www.free-ebooks.net/profile/1561004/789bet
https://pitchwall.co/user/789betruninfo
https://bysee3.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3761380
https://link.space/@789betruninfo
https://my.desktopnexus.com/789betruninfo/
https://git.industra.space/789betruninfo
https://start.me/w/zQmrQa
https://experiment.com/users/789betruninfo
https://www.mountainproject.com/user/201795095/789bet
https://fileforum.com/profile/789betruninfo
https://www.slideserve.com/789betruninfo
https://thefeedfeed.com/rutabaga8686
https://www.gaiaonline.com/profiles/789betruninfo/46656030/
https://gitea.thebrokenrail.com/789betruninfo
http://delphi.larsbo.org/user/789betruninfo
https://www.metooo.io/u/789betruninfo
https://ioby.org/users/derenzistrease769827952
https://letterboxd.com/789betruninfo/
https://visual.ly/users/789betruninfo/portfolio
https://www.callupcontact.com/b/businessprofile/789bet/9020831
https://www.giveawayoftheday.com/forums/profile/182129
https://notabug.org/789betruninfo
https://worldcosplay.net/member/1754275
https://app.talkshoe.com/user/789betruninfo
http://hawkee.com/profile/6651902/
http://www.askmap.net/location/6888427/vietnam/789bet
https://doodleordie.com/profile/89betruninfo
https://www.curioos.com/789betruninfo
https://allmyfaves.com/789betruninfo
https://www.chordie.com/forum/profile.php?id=1932498
https://qooh.me/789betruninfo
https://www.namestation.com/user/derenzistrease769
https://forum.m5stack.com/user/789betruninfo
https://en.bio-protocol.org/userhome.aspx?id=1498667
https://globalcatalog.com/9e8df473fa1c3ceacc144afcd968254bd462589b.vn
https://starity.hu/profil/441723-betruninfo789/
https://jaga.link/https-789betrun.in
https://b.cari.com.my/home.php?mod=space&uid=3060843&do=profile
https://zumvu.com/789betruninfo/
http://molbiol.ru/forums/index.php?showuser=1343192
https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:789betruninfo'>https://netcallvoip.com/wiki/index.php/User:789betruninfo
https://byfc0396.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3951727
https://roomstyler.com/users/789betruninfo
https://www.balatarin.com/users/betruninfo789
https://www.projectnoah.org/users/789betruninfo
https://www.liveinternet.ru/users/betruninfo789/profile
https://www.metooo.it/u/789betruninfo
https://www.exchangle.com/789betruninfo
http://www.invelos.com/UserProfile.aspx?alias=789betruninfo
http://www.travelful.net/location/5424512/vietnam/789bet
https://www.babelcube.com/user/789betrun-info
https://topsitenet.com/profile/789betruninfo/1172058/
https://www.multichain.com/qa/user/789betruninfo
https://sqworl.com/lhlpar
https://www.checkli.com/789betruninfo
https://www.sutori.com/en/user/789betrun-info
https://nhattao.com/members/user6500259.6500259/?tab=selling
https://easyzoom.com/profile/197064/about
https://offcourse.co/users/profile/789betruninfo
https://www.careercup.com/user?id=4863306290954240
https://pixelfed.de/i/web/profile/686851893297803517
https://ok.ru/profile/592188796396
http://www.socialbookmarkssite.com/bookmark/5439710/789bet/
http://www.video-bookmark.com/bookmark/6200052/789bet/
https://pairup.makers.tech/en/789betruninfo
https://edshelf.com/profile/789betruninfo/
https://forum.dzpknews.com/space-uid-691489.html
https://makeprojects.com/profile?activeTab=TabProjectBoards
https://www.ohay.tv/profile/789betruninfo
https://lab.quickbox.io/789betruninfo
https://samkey.org/forum/member.php?286601-789betruninfo
https://apk.tw/space-uid-6306355.html
https://commiss.io/789betruninfo
789betrun.info
Kubet77 hay còn được biết đến với tên gọi Kubet là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến nổi tiếng trên thị trường hiện nay. Mang đến cho người chơi trải nghiệm đa dạng với các trò chơi như xổ số, casino trực tuyến, cá cược bóng đá và nhiều hơn nữa. Trang web này đang rất được ưa chuộng không chỉ tại Việt Nam mà còn trên thị trường quốc tế. Kubet cam kết tiếp tục sáng tạo và phát triển để mang đến những giá trị tốt nhất cho người chơi.
Thông tin nhà cái:
Thương hiệu: Kubet77
Website: https://kubet77.fund/
Địa chỉ: 274 Đ. Đại Mỗ, Nam Từ Liêm, Hà Nội, Việt Nam
Email: kubet77fund@gmail.com
Phone: 0914545680
Hastag: #kubet #nhacaikubet, #kubetcasino, #Kubet77 #kucasino #kubet77fund
https://twitter.com/kubet77fund
https://vimeo.com/kubet77fund
https://www.pinterest.com/kubet77fund/
https://kubet77fund.tumblr.com/
https://www.twitch.tv/kubet77fund
https://500px.com/p/kubet77fund
https://www.reddit.com/user/kubet77fund/
https://www.youtube.com/@kubet77fund
https://www.blogger.com/profile/13946826225521294819
https://gravatar.com/kubet77fund
https://www.openstreetmap.org/user/kubet77fund
https://linktr.ee/kubet77fund
https://archive.org/details/@kubet77fund/
https://www.metal-archives.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.pexels.com/@kubet77-fund-1178614216/
https://hub.docker.com/u/kubet77fund
https://www.mixcloud.com/kubet77fund/
https://about.me/kubet77fund/
https://ko-fi.com/kubet77fund
https://issuu.com/kubet77fund
https://wakelet.com/@kubet77fund
https://circleten.org/a/283950
https://my.archdaily.com/us/@kubet77fund
https://roomstyler.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.speedrun.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.myminifactory.com/users/kubet77fund
https://coolors.co/u/kubet77fund
https://www.deviantart.com/kubet77fund
https://www.intensedebate.com/profiles/kubet77fund
https://pantip.com/profile/8090437
https://coub.com/kubet77fund
https://socialtrain.stage.lithium.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/56772
https://gifyu.com/kubet77fund
https://www.jigsawplanet.com/kubet77fund?viewas=39a00036f4bf
https://www.veoh.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.designspiration.com/kubet77f/saves/
https://influence.co/kubet77fund
https://hypothes.is/users/kubet77fund
https://os.mbed.com/users/kubet77fund/
https://mxsponsor.com/riders/kubet77-fund/about
https://data.world/kubet77fund
https://artistecard.com/kubet77fund
https://triberr.com/kubet77fundv
https://www.webwiki.com/kubet77.fund
https://skitterphoto.com/photographers/91158/kubet77-kubet-casino
https://files.fm/kubet77fund/info
https://experiment.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.mountainproject.com/user/201793483/kubet77-fund
https://anyflip.com/homepage/gjurd
https://tupalo.com/en/users/6563279
https://forum.acronis.com/user/632318
https://www.magcloud.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.provenexpert.com/kubet77fund/
http://www.babelcube.com/user/kubet77-fund
https://www.slideserve.com/kubet77fund
https://www.mapleprimes.com/users/kubet77fund
https://active.popsugar.com/@kubet77fund/profile
https://www.pozible.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://www.instapaper.com/p/kubet77fund
https://trovas.ch/?qa=user/kubet77fund
https://pubhtml5.com/homepage/mizqp/
https://www.silverstripe.org/ForumMemberProfile/show/144922
https://fliphtml5.com/homepage/mdjif/kubet77fund/
https://sketchfab.com/kubet77fund
https://www.reverbnation.com/artist/kubet77fund
https://public.tableau.com/app/profile/kubet77fund/vizzes
https://connect.garmin.com/modern/profile/6926de26-c4ca-4080-b92d-ffed879fc836
https://peatix.com/user/21845450/view
https://readthedocs.org/projects/kubet77fund/
https://www.producthunt.com/@kubet77fund
https://www.credly.com/users/kubet77fund/badges
https://www.walkscore.com/people/933395731765/kubet77fund
https://qiita.com/kubet77fund
https://www.scoop.it/topic/kubet77-fund
https://www.storeboard.com/kubet77fund
https://macro.market/company/kubet77-fund
https://crowdin.com/project/kubet77fund/discussions/2
https://mm.tt/app/map/3248759234?t=GZl1ErrTts
https://www.renderosity.com/users/id:1482932
https://my.desktopnexus.com/kubet77fund/
https://www.fimfiction.net/user/725530/kubet77fund
https://www.free-ebooks.net/profile/1560464/kubet77-fund#gs.848pu7
https://www.copytechnet.com/forums/members/kubet77fund.html
https://forums.alliedmods.net/member.php?u=367108
https://git.qoto.org/kubet77fund
http://hawkee.com/profile/6642173/
https://worldcosplay.net/member/kubet77fund
https://forums.bohemia.net/profile/1232545-kubet77fund/?tab=field_core_pfield_141
https://kubet77fund.gallery.ru/
http://qooh.me/kubet77fund
https://www.multichain.com/qa/user/kubet77fund
https://www.dermandar.com/user/kubet77fund/
https://www.chordie.com/forum/profile.php?id=1931310
https://allmyfaves.com/kubet77fund
https://my.djtechtools.com/users/1402453
https://www.webtoolhub.com/profile.aspx?user=42388614
https://recordsetter.com//user/kubet77fund
https://globalcatalog.com/kubet77fund.vn
https://www.exchangle.com/kubet77fund
https://glose.com/u/kubet77fund
https://www.hebergementweb.org/members/kubet77fund.637825/
https://www.cheaperseeker.com/u/kubet77fund
https://bioimagingcore.be/q2a/user/kubet77fund
https://www.sqworl.com/dex261
https://topsitenet.com/profile/kubet77fund/1171079/
https://www.checkli.com/kubet77fund
https://git.project-hobbit.eu/kubet77fund
https://www.rctech.net/forum/members/kubet77fund-365591.html
https://git.metabarcoding.org/kubet77fund
http://www.video-bookmark.com/bookmark/6198071/kubet77fund/
https://leetcode.com/kubet77fund/
http://www.fanart-central.net/user/kubet77fund/profile
https://www.fitday.com/fitness/forums/members/kubet77fund.html
https://www.iniuria.us/forum/member.php?430251-kubet77fund
https://www.ohay.tv/profile/kubet77fund
https://wibki.com/kubet77fund
https://jii.li/jSqCu
https://kubet77fund.mypixieset.com/
http://prsync.com/kubetfund/
https://www.vevioz.com/kubet77fund
https://demo.wowonder.com/kubet77fund
https://www.namestation.com/user/xumurazordrdostol
https://forum.m5stack.com/user/kubet77fund
https://ourairports.com/members/kubet77fund/
https://connect.gt/user/kubet77fund
https://teletype.in/@kubet77fund
https://noti.st/kubet77fund
https://link.space/@kubet77fund
https://ioby.org/users/xumurazordrdostol827532
https://www.aicrowd.com/participants/kubet77fund
https://lwccareers.lindsey.edu/profiles/4548955-kubet77-fund
https://lab.quickbox.io/kubet77fund
https://gitlab.aicrowd.com/kubet77fund
https://heylink.me/kubet77fund/
http://winnipeg.pinklink.ca/author/kubet77fund/
https://www.wpgmaps.com/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://www.viewbug.com/member/kubet77fund
https://www.asklent.com/user/kubet77fund
https://pytania.radnik.pl/uzytkownik/kubet77fund
http://www.anibookmark.com/user/kubet77fund.html
https://www.notebook.ai/@kubet77fund
https://matkafasi.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.fundable.com/user-875469
https://linklist.bio/kubet77fund
https://slot.bio/kubet77fund
https://www.bandlab.com/kubet77fund
https://www.printables.com/@kubet77fund_1997501
https://disqus.com/by/kubet77kubetcasino/about/
https://www.metooo.it/u/kubet77fund
https://bit.ly/4aE7QHO
https://chart-studio.plotly.com/~kubet77fund
https://booklog.jp/users/kubet77fund/profile
https://code.getnoc.com/kubet77fund
https://gitlab.pavlovia.org/kubet77fund
https://www.hahalolo.com/@kubet77fund
https://kktix.com/user/5919689
https://lu.ma/u/usr-cd2kFhVvB9haCbQ
https://photoclub.canadiangeographic.ca/profile/21245460
https://www.longisland.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://community.alteryx.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/570585
https://vocal.media/authors/kubet77-fund
https://forum.liquidbounce.net/user/kubet77fund/
https://qna.habr.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.foroatletismo.com/foro/members/kubet77fund.html
https://www.outdoorproject.com/users/xumurazordrdostol520955
https://zumvu.com/kubet77fund/
https://communities.bentley.com/members/354daac4_2d00_db4e_2d00_4b98_2d00_9b7f_2d00_2d54fcd48313
https://www.penname.me/@kubet77fund
https://hackerone.com/kubet77fund
https://phijkchu.com/a/kubet77fund/video-channels
https://phijkchu.com/c/kubet77_fund/videos
https://infogram.com/kubet77fund-1hnp27empg1on4g?live
http://gendou.com/user/kubet77fund
https://py.checkio.org/class/kubet77-fund/
https://amazingradio.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://dreevoo.com/profile_info.php?pid=628832
http://freestyler.ws/user/451560/kubet77fund
https://audiomack.com/kubet77fund
http://emseyi.com/user/kubet77fund
https://hangoutshelp.net/user/kubet77fund
http://planforexams.com/q2a/user/kubet77fund
https://bikeindex.org/users/5--p6fuen01ydhjd1jfqmg
https://filmow.com/usuario/kubet77fund
https://rotorbuilds.com/profile/37698/
https://samkey.org/forum/member.php?286505-kubet77fund
https://studynotes.ie/posts/JgI9yn-kubet77fund
https://velopiter.spb.ru/profile/111144-kubet77fund/?tab=field_core_pfield_1
https://vjudge.net/user/kubet77fund
https://web.ggather.com/kubet77fund
https://willysforsale.com/author/kubet77fund
https://www.circleme.com/kubet77fund
https://b.cari.com.my/home.php?mod=space&uid=3053604&do=profile
https://www.guilded.gg/u/kubet77fund
https://www.nintendo-master.com/profil/kubet77fund
https://www.cakeresume.com/me/kubet77fund
https://satori.lv/profile/-36100
https://schoolido.lu/user/kubet77fund/
https://promosimple.com/ps/2bbf5/kubet77fund
https://ww3.lectulandia.co/foros/users/kubet77fund
https://www.inflearn.com/users/1379578
https://storyweaver.org.in/en/users/916467
https://allmy.bio/kubet77fund
https://portfolium.com/kubet77fund
https://velog.io/@kubet77fund/about
https://www.diigo.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.kickstarter.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://www.metooo.io/e/kubet77fund
https://www.metooo.io/u/kubet77fund
https://www.quia.com/profiles/kubet77fund
https://pinshape.com/users/4040960-kubet77fund
https://visual.ly/users/kubet77fund/portfolio
https://www.zotero.org/kubet77fund/cv
https://able2know.org/user/kubet77fund/
https://8tracks.com/kubet77fund
https://www.bitsdujour.com/profiles/HPKYPO
https://telegra.ph/kubet77fund-04-18
https://atlanta.bubblelife.com/community/kubet77fund
https://jsfiddle.net/kubet77fund/pf7Lq5oe/
https://band.us/band/94633541/intro
https://englishbaby.com/findfriends/gallery/detail/2496129
https://fileforum.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://www.beatstars.com/xumurazordrdostol/about
https://www.weddingbee.com/members/kubet77fund/
https://www.gaiaonline.com/profiles/kubet77fund/46656111/
https://myonlinestudybuddy.com/members/kubet77fund/profile/
https://rentry.co/gxu4zmar
https://www.diggerslist.com/kubet77fund/about
https://scrapbox.io/kubet77fund/kubet77fund
https://www.proarti.fr/account/kubet77fund
https://etextpad.com/v5wi5sjyse
https://www.espace-recettes.fr/profile/kubet77fund/657802
https://inkbunny.net/kubet77fund
https://www.themesindep.com/support/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://www.mtg-forum.de/user/75887-kubet77fund/
https://www.furaffinity.net/user/kubet77fund
https://www.elephantjournal.com/profile/kubet77fund/
https://padlet.com/xumurazordrdostol/kubet77fund-jolnkfleg51ywkro
https://justpaste.it/u/kubet77fund
https://justpaste.it/egekj
https://hashnode.com/@kubet77fund
https://kubet77fund.hashnode.dev/kubet77fund
https://guides.co/g/kubet77fund/370485
https://micro.blog/kubet77fund
https://kubet77fund.micro.blog/about
https://confengine.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.bigbasstabs.com/profile/92233.html
https://play.eslgaming.com/player/myinfos/20044979/
https://research.openhumans.org/member/kubet77fund/
https://webarticleservices.com/members/kubet77fund
http://mayfever.crowdfundhq.com/users/kubet77-fund
https://myanimeshelf.com/profile/kubet77fund
https://anantsoch.com/members/kubet77fund/profile/
https://www.huntingnet.com/forum/members/kubet77fund.html
https://www.rcuniverse.com/forum/members/kubet77fund.html
https://www.bark.com/en/us/company/kubet77-fund/oRq8N/
http://www.worldchampmambo.com/UserProfile/tabid/42/userId/378965/Default.aspx
https://www.divephotoguide.com/user/kubet77fund
https://wakelet.com/wake/AJ_yi-0wSol5QxbzCNyTJ
https://www.funddreamer.com/users/kubet77-fund
https://www.openhumans.org/member/kubet77fund
http://maisoncarlos.com/UserProfile/tabid/42/userId/1934416/Default.aspx
https://offcourse.co/users/profile/kubet77fund
http://magic.ly/kubet77fund
http://forums.visualtext.org/member.php?action=profile&uid=1150659
https://pandoraopen.ru/author/kubet77fund
https://www.11secondclub.com/users/profile/1583216
https://hanson.net/users/kubet77fund
http://www.socialbookmarkssite.com/bookmark/5439383/kubet77fund/
https://glitch.com/@kubet77fund
https://git.industra.space/kubet77fund
https://git.industra.space/kubet77fund/kubet77fund/issues/1
http://www.invelos.com/UserProfile.aspx?alias=kubet77fund
http://compcar.ru/forum/member.php?u=110494
https://app.talkshoe.com/user/kubet77fund
http://vetstate.ru/forum/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=113721
https://en.bio-protocol.org/userhome.aspx?id=1498687
https://nexusconsultancy.co.uk/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://articledirectoryzone.com/members/kubet77fund/
https://comicsdb.cz/profil/39067/kubet77fund
https://easyzoom.com/profile/197048/about
https://developer.tobii.com/community-forums/members/kubet77fund
https://www.facer.io/u/kubet77fund
https://www.emoneyspace.com/kubet77fund
https://electrodb.ro/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://fontstruct.com/fontstructors/2427333/kubet77fund
https://www.fullhires.com/author/kubet77fund/
https://hackmd.io/@kubet77fund/ByrTt9kbA
https://varecha.pravda.sk/profil/kubet77fund/o-mne/
https://www.careercup.com/user?id=6287139489185792
https://manylink.co/@kubet77fund
https://mecabricks.com/en/user/kubet77fund
https://gitlab.vuhdo.io/kubet77fund
https://twitback.com/kubet77fund
https://drivehud.com/forums/users/xumurazordrdostol
https://iglinks.io/xumurazordrdostol-zwa
https://vacationinsiderguide.com/user/kubet77fund
https://kaeuchi.jp/forums/users/kubet77fund/
https://kubet77fund.gitbook.io/kubet77fund/
http://dtan.thaiembassy.de/uncategorized/2562/?mingleforumaction=profile&id=178135
www.biblesupport.com/user/581832-kubet77fund/
https://wmart.kz/forum/user/158848/
https://because-gus.com/forums/participants/kubet77fund
https://www.are.na/kubet77-fund/kubet77fund
https://vws.vektor-inc.co.jp/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://www.fantasyplanet.cz/diskuzni-fora/users/kubet77fund
https://www.inventoridigiochi.it/membri/kubet77fund/profile/
https://www.shippingexplorer.net/en/user/kubet77fund/104578
https://pairup.makers.tech/en/kubet77fund
https://original.misterpoll.com/users/5425724
https://www.serialzone.cz/uzivatele/210065-kubet77fund/
https://git.forum.ircam.fr/kubet77fund
https://emplois.fhpmco.fr/author/kubet77fund/
https://www.giveawayoftheday.com/forums/profile/182244
https://gitlab.nic.cz/kubet77fund
https://help.orrs.de/user/kubet77fund
https://www.kfz-betrieb.vogel.de/community/user/kubet77fund
https://eternagame.org/players/368647
https://spiderum.com/nguoi-dung/kubet77fund
https://www.freelistingusa.com/listings/kubet77fund
https://t.ly/At51H
https://cadillacsociety.com/users/kubet77fund
https://www.pixiv.net/en/users/105396125
https://hub.safe.com/publishers/kubet77fund?page=1&page_size=10
https://www.fz.se/medlem/344678
https://themepacific.com/support/users/xumurazordrdostol
https://community.fyers.in/member/99QB8zrg5R
https://www.tzportfolio.com/help/forum/profile/kubet77fund.html
https://s.id/254WG
https://m.wibki.com/kubet77fund
https://www.kniterate.com/community/users/kubet77fund
http://l-avt.ru/support/dialog/?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=65483
https://code.datasciencedojo.com/kubet77fund
https://linkmix.co/22686132
https://mobilizon.envs.net/events/91b29e35-b485-486a-a0d1-e0b7143eb4bf
https://www.photofrnd.com/kubet77fund
https://www.strata.com/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://www.dokkan-battle.fr/forums/users/kubet77fund/
https://chillspot1.com/user/kubet77fund
https://pledgeit.org/preview/6622234882210a3d04ec0782
https://codepad.co/kubet77fund
https://bom.so/Qc6344
https://www.spigotmc.org/members/kubet77fund.2010815/
https://motion-gallery.net/users/598264
https://notabug.org/kubet77fund
https://notabug.org/kubet77fund/kubet77fund/issues/1
https://www.recentstatus.com/kubet77fund
https://www.curioos.com/kubet77fund
https://wperp.com/users/kubet77fund
https://lookingforclan.com/user/kubet77fund
https://v.gd/AzYiDk
https://writexo.com/yue6j6p2
https://agoracom.com/members/kubet77fund
http://test.sozapag.ru/forum/user/234824/
https://phenomenalarticles.com/members/kubet77fund
http://www.schoolpress.ru/news_schoolpress/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=211157
https://glamorouslengths.com/author/kubet77fund
https://hcgdietinfo.com/hcgdietforums/members/kubet77fund/
https://www.blackhatprotools.info/member.php?187286-kubet77fund
https://hukukevi.net/user/kubet77fund
https://offroadjunk.com/questions/index.php?qa=user&qa_1=kubet77fund
https://designaddict.com/community/profile/kubet77fund
https://healthinsiderguide.com/user/kubet77fund
https://www.hivizsights.com/forums/users/xumurazordrdostol/
https://linkr.bio/kubet77fund
https://www.sutori.com/en/user/kubet77-fund
https://nextion.tech/forums/users/kubet77fund/
https://graphcommons.com/u/kubet77fund
http://bluerevolutioncrowdfunding.crowdfundhq.com/users/kubet77-fund
https://www.riptapparel.com/pages/member?kubet77fund
http://delphi.larsbo.org/user/kubet77fund
https://www.czporadna.cz/user/kubet77fund
https://ekonty.com/-kubet77fund#info
https://www.logic-sunrise.com/forums/user/118477-kubet77fund/
https://biiut.com/kubet77fund
https://aleratrading.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=140059
https://app.scholasticahq.com/scholars/278432-kubet77-fund
http://www.4mark.net/story/11958232/kubet77fund
https://www.tadalive.com/kubet77fund
https://byfc0396.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3952066
https://bysee3.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=3761241
http://www.fjclwz.us/upload/home.php?mod=space&uid=2301711
https://zmxw.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2651817
https://www.barracudaforums.com/forum/members/11383-kubet77fund.html
https://themecentury.com/forums/users/kubet77fund
https://cointr.ee/kubet77fund
https://mississaugachinese.ca/home.php?mod=space&uid=1271107
https://dlive.tv/kubet77fund
https://bandori.party/user/198869/kubet77fund/
https://sanjose.granicusideas.com/ideas/kubet77fund
https://www.bestadsontv.com/profile/463119/Kubet77-Fund
https://tvchrist.ning.com/profile/Kubet77Fund
https://iszene.com/user-222857.html
https://imageevent.com/kubet77fund
https://profile.hatena.ne.jp/kubet77fund/
Kubet77 – Trang Chủ Nhà Cái Kubet Casino Chính thức, không bị chặn. Sản phẩm Game trực tuyến cuốn hút, bao gồm : Esports, Xóc Dĩa, Slot Games, Roulette, Thể thao...
kubet77.fund