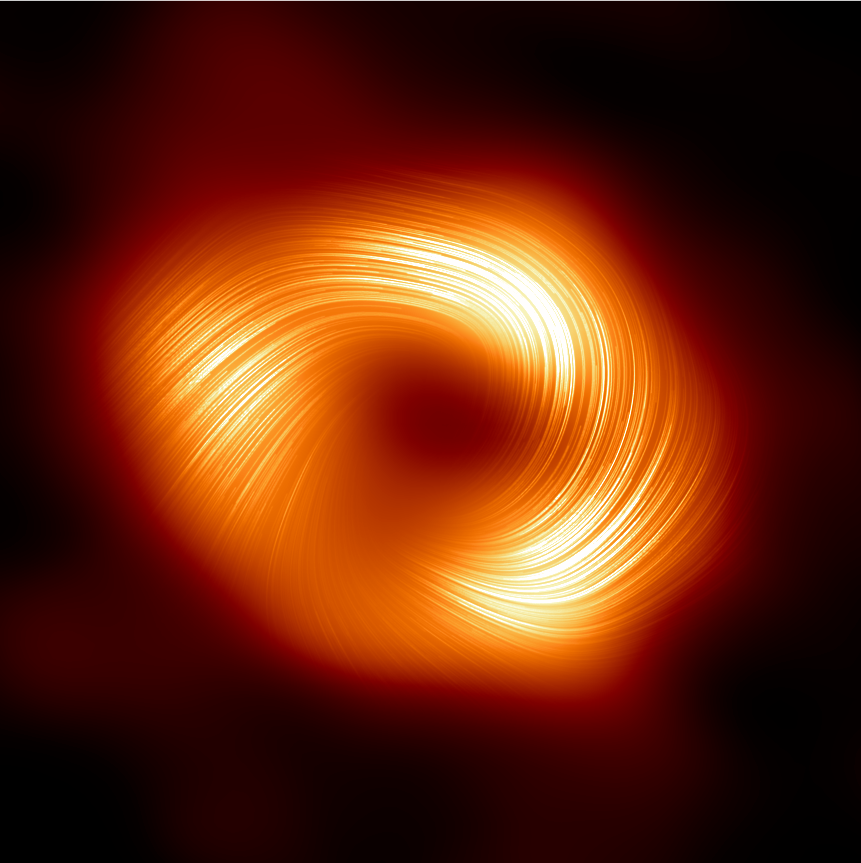
NRAO - Astronomers Unveil Strong Magnetic Fields Spiraling at the Edge of Milky Way’s Central Black Hole:
https://public.nrao.edu/news/astronomers-unveil-strong-magnetic-fields-spiraling-at-the-edge-of-milky-ways-central-black-hole/
#EventHorizonTelescope #EHT #ALMA #PolarizedLight #RadioWave #SagittariusA #BlackHole #MagneticField #MatterJet #Astrophysics #Astronomy
People
Circles
Posts
Robert Lea - James Webb Space Telescope finds dwarf galaxies packed enough punch to reshape the entire early universe:
https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-dwarf-galaxies-cosmic-evolution
#DwarfGalaxy #JamesWebb #JWST #GravitationalLensing #Abell2744 #BigBangTheory #BigBang #Reionization #GeneralRelativity #Relativity #Cosmology #Astrophysics #Astronomy
Rahul Rao - The Milky Way's enormous, star-studded 'Radcliffe Wave' is literally waving:
https://www.space.com/radcliffe-wave-waving-milky-way
#RadcliffeWave #InterstellarGas #StarFormation #Astrophysics #Astronomy
Videos
People
Circles
Videos
Posts
NRAO - Astronomers Unveil Strong Magnetic Fields Spiraling at the Edge of Milky Way’s Central Black Hole:
https://public.nrao.edu/news/astronomers-unveil-strong-magnetic-fields-spiraling-at-the-edge-of-milky-ways-central-black-hole/
#EventHorizonTelescope #EHT #ALMA #PolarizedLight #RadioWave #SagittariusA #BlackHole #MagneticField #MatterJet #Astrophysics #Astronomy
Robert Lea - James Webb Space Telescope finds dwarf galaxies packed enough punch to reshape the entire early universe:
https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-dwarf-galaxies-cosmic-evolution
#DwarfGalaxy #JamesWebb #JWST #GravitationalLensing #Abell2744 #BigBangTheory #BigBang #Reionization #GeneralRelativity #Relativity #Cosmology #Astrophysics #Astronomy
Rahul Rao - The Milky Way's enormous, star-studded 'Radcliffe Wave' is literally waving:
https://www.space.com/radcliffe-wave-waving-milky-way
#RadcliffeWave #InterstellarGas #StarFormation #Astrophysics #Astronomy
The Johns Hopkins University APL - NASA’s New Horizons Detects Dusty Hints of an Extended Kuiper Belt:
https://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/News-Article.php?page=20240220
#NewHorizons #NASA #KuiperBelt #VenetiaBurney #DustCounter #InterplanetaryDust #Dust #KuiperBeltObject #KuiperBelt #KBO #SolarSystemScience #Astrophysics #Astronomy
NASA’s New Horizons Team Calls for the Amateur Astronomical Community to Augment the Mission’s Observations of Uranus and Neptune
pluto.jhuapl.edu
Markus Bernards - A star like a Matryoshka doll: New theory for gravastars:
https://phys.org/news/2024-02-star-matryoshka-doll-theory-gravastars.html
#BlackHole #GravitationalCondensate #Gravastar #MatryoshkaDoll #Relativity #QuantumMechanics #Astrophysics #Physics